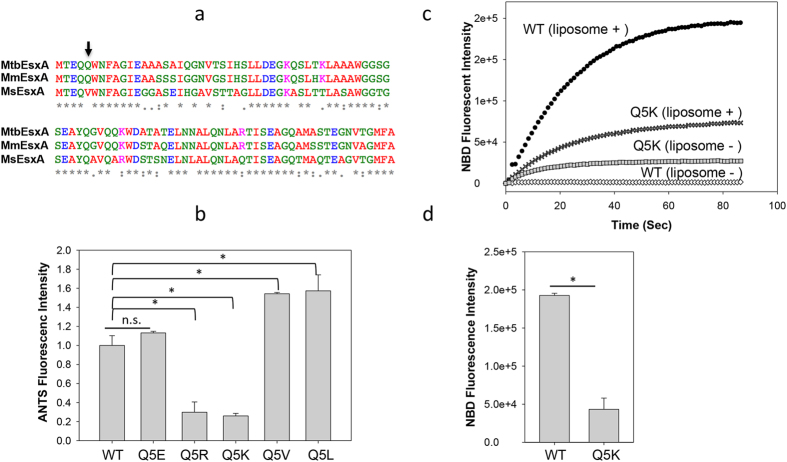
Figure 1. Mutations at Q5 up or down regulated the membrane-permeabilizing activity of MtbEsxA.
(a) The sequence alignment of MtbEsxA, MmEsxA and MsEsxA. The residues are colored according to chemical nature: Red (hydrophobic), Green (polar), Blue (acidic) and Magenta (basic). Arrow: the Q5 position. (b) 6 μM of the indicated proteins were injected into the liposome solutions at pH 4.0. The relative membrane-permeabilizing activity was measured as ANTS fluorescence dequenching at 60 s of post-injection and quantified from at least three independent experiments. The data were presented as mean ± S.E. (n = 5, *p < 0.05). (c) The NBD-labeled EsxA(WT) or EsxA(Q5K) protein was incubated with or without liposomes in 20 mM TrisHCl, 100 mM NaCl (pH 7) for 30 min. Subsequently, the solution was rapidly acidified by adding 0.1 volume of 1 M NaAc (pH 4). The solution was continuously stirred in the cuvette. NBD fluorescence emission was recorded as a function of time. The representative curves from at least three repeats were shown. (d) The NBD emission intensity at 90 s post-acidification was calculated from three independent experiments. The background signals (liposome -) were subtracted from the signals with liposome (liposome+). The data is presented as mean ± S.E. (n = 3, *p < 0.05).