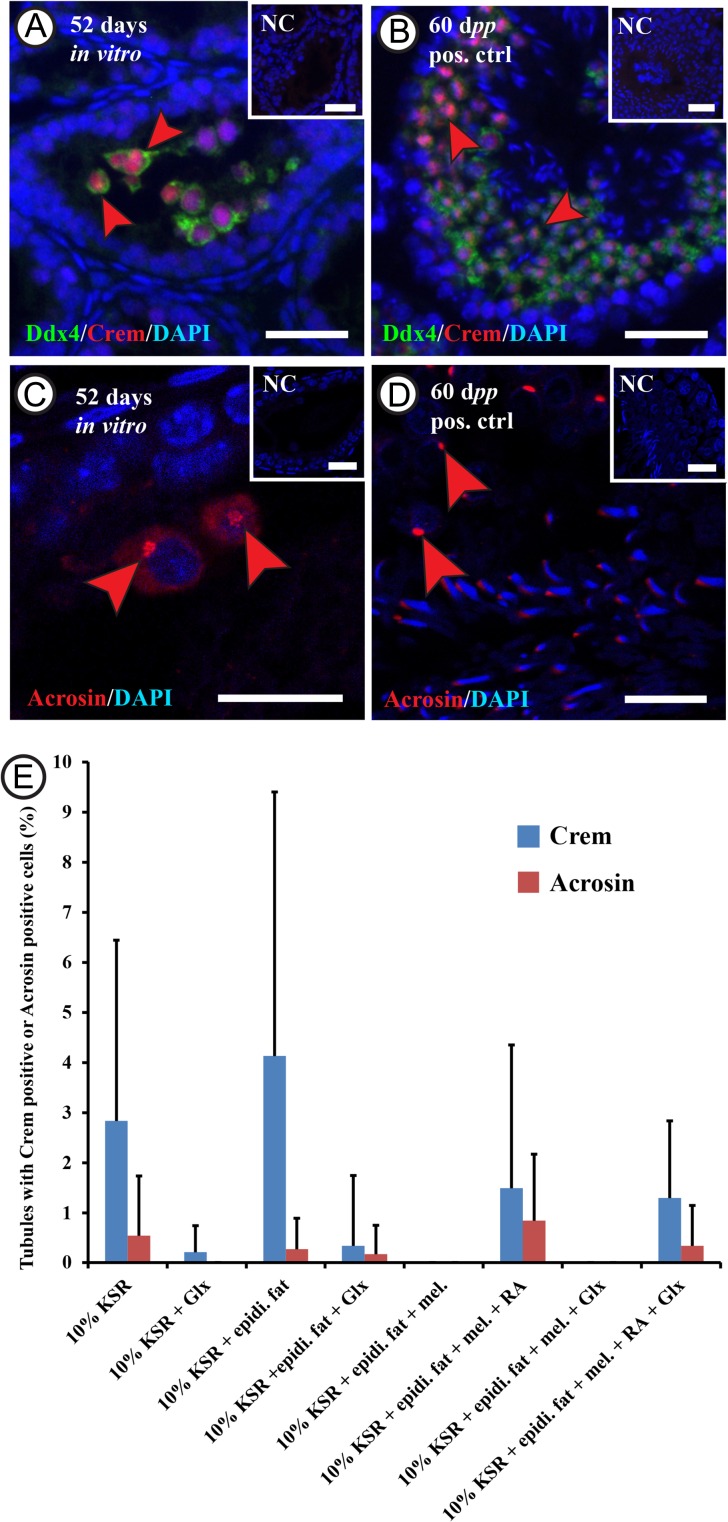
Figure 4.
Assessment of the rat male germ cell differentiation in vitro.Double immunofluorescent staining for 5 days postpartum (dpp) rat testicular tissue after culturing in minimum essential medium alpha (MEMα) + 10% (v/v) knock-out serum replacement (KSR) for 52 days, showing cells double positive for Ddx4 (DEAD box polypeptide 4; in green) and Crem (cAMp (cyclic adenosine mono phosphate) response element modulator; in red) labeled with red arrowheads (A and B), and Acrosin positive cells (in red) labeled with the red arrowheads (C and D). Rabbit IgGs were used instead of the primary antibodies in the negative control and DAPI (4’,6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole) was utilized in counterstaining (in blue). The scale bars are 20 µm A and B, and negative controls), and 10 µm (C and D). The graph (E) shows the percentage of tubules containing Crem positive cells (in blue) or Acrosin positive cells (in red) after culturing the 5 dpp rat testicular tissue for 52 days in the different culture conditions. Values are mean ± SD (n = 3–12 (Crem), n = 3–9 (Acrosin)). For statistical analysis, ANOVA on ranks test was applied to compare between the percentages of tubules from the different culture conditions. Abbreviations: minimal essential medium α (MEMα), melatonin (mel.), knock-out serum replacement (KSR), Glutamax (Glx), epididymal fat (epidi. fat), and retinoic acid (RA).