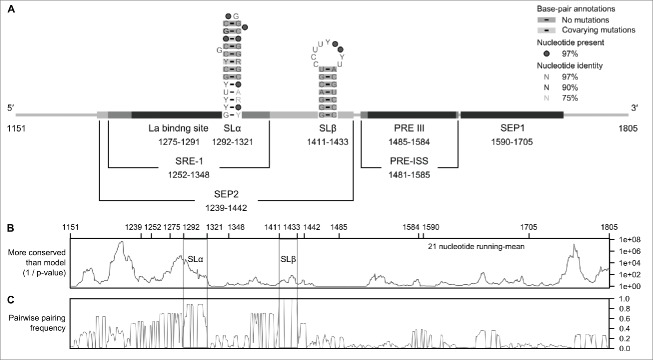
Figure 2.
Functional elements and RNA secondary structures within the PRE. (A) A Map of the known functional elements and RNA secondary structures of HBV PRE. HBV (RefSeq: NC_003977.1; GenBank: X04615.1) PRE contains 2 major nuclear export elements, recently named SEP1 (nucleotides 1590-1705) and SEP2 (nucleotides 1239-1442).10 SEP1 contains the binding site for ZC3H18, a cellular factor for PRE-mediated nuclear export. SEP2 contains previously described SRE-1 (nucleotides 1252-1348),12 La binding site (nucleotides 1275-1291),34 SLα (nucleotides 1292-1321) and SLβ (nucleotides 1411-1433).4 The PRE intronic splicing silencer (PRE-ISS)35 region encompasses PRE III (nucleotides 1458-1584).36 The PRE III is a binding site for GAPDH and an alternative splicing regulator, polypyrimidine tract binding protein (PTB). PTB is also a cellular factor for a PRE-mediated nuclear export activity. The secondary structures of SLα and SLβ were inferred from NMR data (PDB: 2JYM)17 and/or previous mutation analyses.4,13 (B) Plot of conservation for an aligned, annotated, representative set of human HBV genotypes A-H (n = 32)16 and woodchuck hepadnavirus (n = 9) sequences. The p-value plot was produced by CDS-plotcon,30 in which the probability of the conservation in a 21 nucleotide running-mean is as great or greater than what is expected from a null model using a default "non-coding" setting. The gray boxes indicate the nucleotide positions for SLα and SLβ. (C) Plot of the frequencies of conserved paired sites (predicted RNA secondary structures) that was done using pairwise comparisons on the same set of aligned sequences (n = 41). The analysis was done using StructureDist in the SSE package,31 in which the maximum value of each frequency is equal to 1.