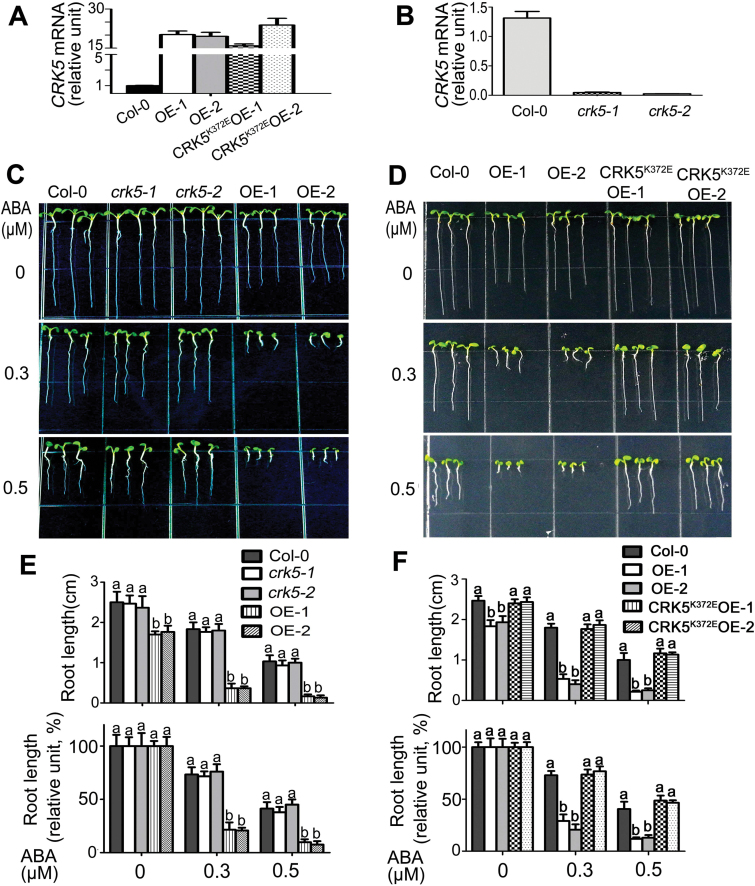
Fig. 1.
Overexpression of CRK5, but not its mutated form CRK5 K372E, results in an ABA-hypersensitive phenotype in early seedling growth. (A) Real-time PCR analysis of the transgenic lines overexpressing CRK5 (OE-1 and OE-2) or a mutated form of CRK5 encoding CRK5K372E with a point mutation at its kinase domain (CRK5K372E OE-1 and OE-2). Expression level of CRK5 or CRK5 K372E was normalized to that of Actin2/8, and the expression level of CRK5 in Col-0 was set to 1. Values are the mean±SE of three independent biological determinations, and different letters represent significant differences at P<0.05 (Duncan’s multiple range test). (B) Real-time PCR analysis of the CRK5 expression level in wild-type Col-0, and crk5-1 and crk5-2 T-DNA insertion mutant plants. Values are the mean±SE of three independent biological determinations, and different letters represent significant differences at P<0.05 (Duncan’s multiple range test). (C, D) Root growth of wild-type Col-0, crk5-1, crk5-2, OE-1, OE-2 (C) or Col-0, OE-1, OE-2, CRK5K372EOE-1 and CRK5K372EOE-2 (D) growing on ABA-free (0 μM) or (±)ABA-containing (0.3 and 0.5 μM) MS medium. Seeds were directly planted in the medium for a 72-h stratification and germinating seeds/young seedlings continued to grow for 10 d before investigation. The experiments were repeated three times with similar results. (E, F) Statistical analysis of absolute (top) and relative values (bottom) of root length of different genotypes described in (C) and (D), respectively. Relative values of the root length of each genotype grown on MS medium containing 0.3 and 0.5 μM (±)ABA are normalized relative to the value of the corresponding genotype at 0 μΜ (±)ABA, which is taken as 100%. Values are the mean±SE of three biological determinations, and different letters represent significant differences at P<0.05 (Duncan’s multiple range test).