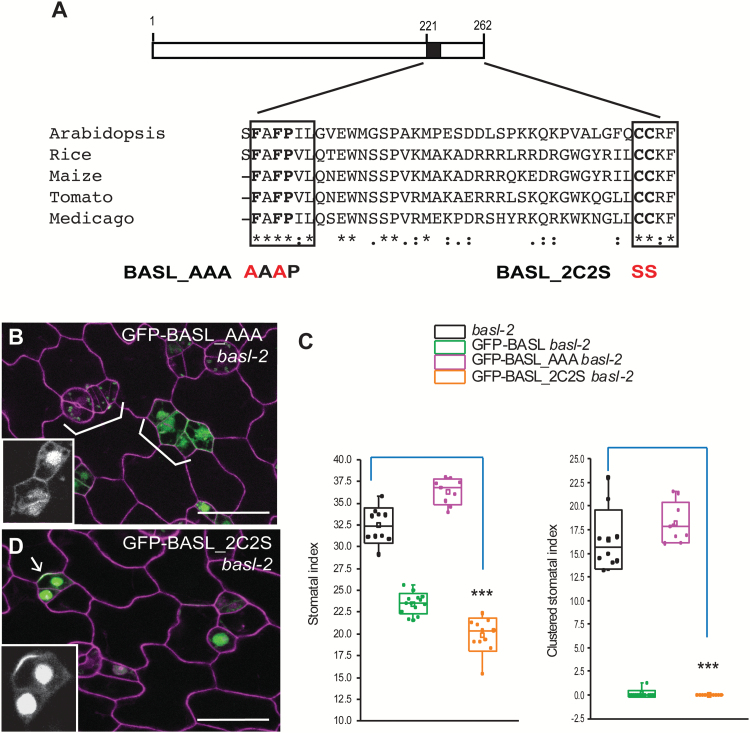
Fig. 3.
Two conserved amino acids are critical.
(A) Boxed diagram demonstrates the conserved C-terminal domain of BASL. The black box marks the critical small motif for BASL polarity formation. The last 41 amino acids align with a few BASL-like proteins from other plant species. Two conserved motifs, FAFPI/VL and CCR/KF, are indicated with boxes. BASL_AAA and BASL_2C2S were generated by mutating FAF to AAA and CC to SS, respectively. Red indicates site mutations. (B) Confocal image to show that GFP-BASL_AAA (green) totally lost polarization. Cell outlines were stained with PI (magenta). White brackets point to clustered stomata, suggesting the basl-2 phenotype was not rescued. Scale bar = 25 µm. (C) Quantification of stomatal phenotype in 5-dpg adaxial cotyledons. GFP-BASL_2C2S, but not GFP-BASL_AAA, complemented the stomatal defects in basl-2. (Mann–Whitney test, ***P < 0.001 compared to basl-2). (D) GFP-BASL_2C2S (green) is polarized and functional in basl-2. Insets in B and D show representative protein localization (GFP channel only). Arrow points to protein polarization. Scale bar = 25 µm.