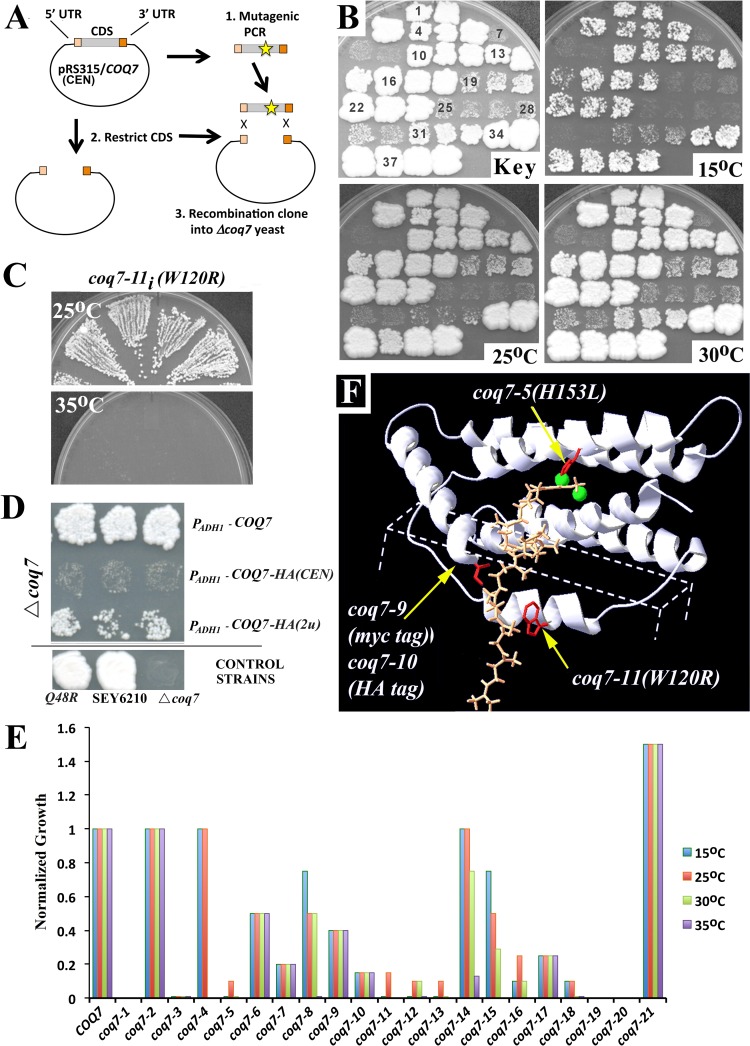
Fig 1. Generation and Characterization of a coq7 Hypomorphic Allelic Series.
(A) Strategy for generating mutant coq7 alleles: coq7-19(Δcoq7) yeast were transformed with a mix of PCR mutagenized coq7 constructs and then hypomorphic alleles identified by slow growth on 3% ethanol (YEPE3%). (B) Mutagenized clones were patched in triplicate, then replica plated onto YEPE3%, and monitored for growth at 15°C, 25°C and 30°C (top left panel shows patch numbering) relative to wild type SEY6210 yeast (patches #37–39). Alleles of interest are described in full in S1 Table and include: coq7-6 (patches # 13–15); coq7-11 (# 19–21); coq7-13 (# 25–27); coq7-5 (# 28–30); coq7-16 (# 31–33) and coq7-2(Q48R) (# 34–36). (C) The coq7-11 allele is temperature-sensitive and inviable at 35°C when integrated back into the wild type COQ7 locus. Shown are four independent re-integrants. (D) Addition of a HA or myc epitope tag to the C-terminus of wild type Coq7p results in hypomorphic growth on YEPE3%. Shown also is the effect of COQ7 copy number (CEN—low and 2μ- high) and promoter identity (ADH1 vs. native) on growth at 30°C YEPE3% (10 days). PADH1-COQ7-HA(CEN) was used for the library screen described in Fig 2. coq7-2(Q48R) grows indistinguishably from wild type at 30°C. (E) Relative growth rate of mutant coq7 alleles versus wild type yeast (SEY6210) cultured at four different temperatures– 15°C, 25°C, 30°C and 35°C (refer to Table 1 for allele identification, and S1 Table for raw data). Data is normalized to SEY6210 cell density at late log phase, for each respective temperature. Data for coq7-5, coq7-15 and coq7-16 at 35°C was not collected. (F) Location of relevant amino acid disruptions caused by various hypomorphic coq7 alleles (labeled). Changes affect highly conserved residues (red) and have been mapped onto a model of monomeric rat CLK-1/Coq7p [21]. Shown is the predicted position of the conserved C-terminus submerged in the mitochondrial inner membrane (dotted box), the di-iron-containing active site (green) and the DMQ6 substrate loaded into the active site (saffron). Coq7 dimerizes [35] and we have previously provided a model of dimeric rat CLK-1 [21].