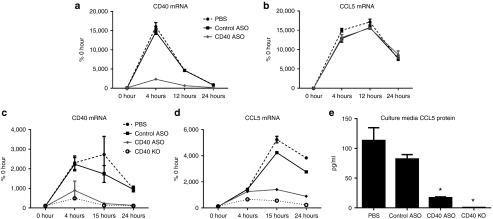
Figure 2.
In vitro incubation of thioglycollate-elicited peritoneal macrophages with CD40 antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) reduced CD40 and CD40-dependent inflammation. To evaluate CD40 ASO activity following a broad induction of inflammatory pathways, macrophages were incubated with 10 μmol/l of ASO for 1 hour, washed and then cells were harvested 4, 12, and 24 hours following 0.5 μg/ml lipopolysaccharide and (a) CD40 and (b) CCL5 quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) were performed. To evaluate CD40 ASO activity following CD40-dependent inflammation, macrophages were incubated with 10 μmol/l of ASO for 1 hour, washed and then cells were harvested 4, 12, and 24 hours following 100 ng/ml IFN-γ + 10 μg/ml of an activating CD40 mAb and (c) CD40 and (d) CCL5 qRT-PCR were performed. (e) Media removed from the ASO-treated cells exposed to IFN-γ and the CD40 mAb treatments were used for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay determination of CCL5. Mean ± SEM, n = 3/treatment and timepoint, *P < 0.05 versus phosphate buffered saline control.