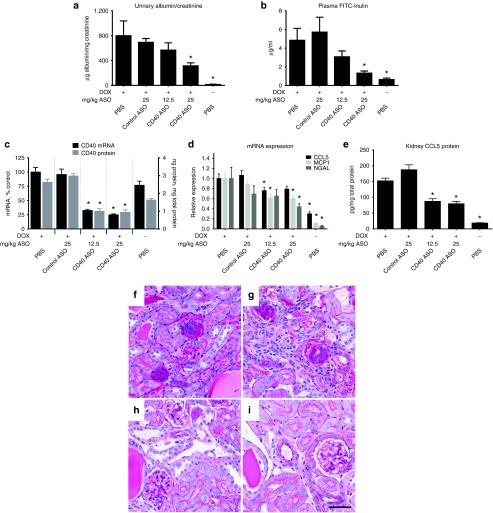
Figure 4.
CD40 ASO treatment mitigated DOX nephropathy. CD40 antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) and control ASO treatments were initiated 2 weeks following initiation of DOX nephropathy and after 8 weeks of ASO treatments renal functional assessments of (a) proteinuria (graphed as the ratio of the urine albumin to creatinine) and (b) plasma fluorescein isothicyanate conjugated inulin (FITC)-inulin elimination (assessed by a single measurement of residual plasma FITC-Inulin two hours following FITC-inulin injection) were performed. Additionally, kidneys were harvested and whole kidney (c) CD40 mRNA and protein, (d) CCL5, MCP-1 and NGAL mRNA, and (e) CCL5 protein were measured. (f–i) Periodic acid-Schiff staining of representative kidney sections from (f) phosphate buffered saline (PBS), (g) control ASO, (h) 12.5 mg/kg CD40 ASO, and (i) 25 mg/kg CD40 ASO groups. Mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05 versus Dox PBS group, n = 10–12/group (DOX mice) or 6/group (healthy control mice), scale bar = 50 μm.