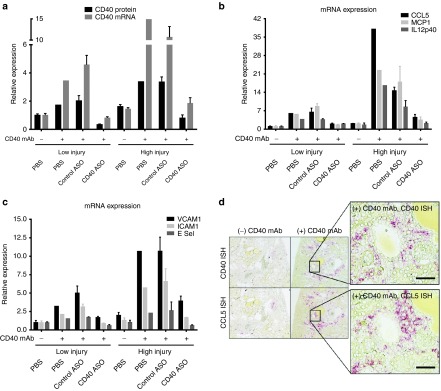
Figure 6.
Kidney CD40-dependent inflammation, increased in DOX nephropathy, was attenuated by CD40 antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) treatments. Following 10.5 mg/kg DOX, mice were divided into those with exhibiting low or high DOX injury based on body weight change and proteinuria. Three 25 mg/kg ASO treatments were then given 29, 33, and 36 days following the DOX administration. Next, the activating CD40 mAb was given on day 39 and kidneys were harvested on day 40. (a) CD40 protein and mRNA measurements (b and c) and CD40-dependent inflammation were measured from whole kidney quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analyses. (d) CD40 and CCL5 in situ hybridization in kidneys from high DOX injury mice in the absence or presence of the CD40 mAb. Data are normalized to low injury (−) CD40 mAb phosphate buffered saline (PBS) = 1.0. Mean ± SEM, n = 1–3/group, scale bar = 50 μm.