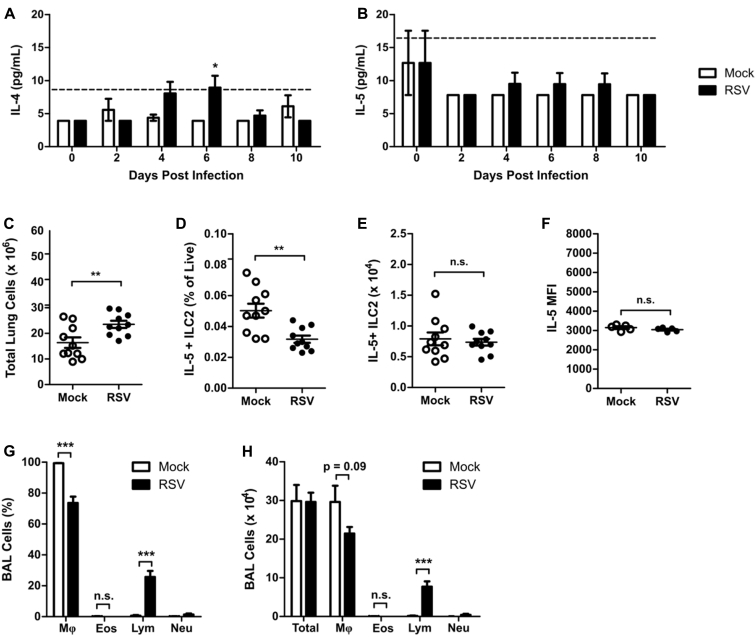
Fig E2.
RSV does not induce IL-5–producing ILC2s. WT mice were infected with 3 × 106 PFU of RSV strain 01/2-20 and harvested on days 0 to 10 after infection. A and B, ELISA for IL-4 (Fig E2, A) and IL-5 (Fig E2, B) in whole-lung homogenate. C, Total number of live cells in the lungs at day 4 after infection. D, IL-5+ ILC2s as a percentage of viable cells as measured by using flow cytometry at day 4 after infection. E, Total number of IL-5+ ILC2s as measured by using flow cytometry at day 4 after infection. F, MFI of IL-5 staining in ILC2s as measured by using flow cytometry at day 4 after infection. G, Percentage of cells in BAL fluid at day 4 after infection. H, Total number of cells in BAL fluid at day 4 after infection. Data are plotted as means ± SEMs. For Fig E2, A and B, n = 8-14 mice per group combined from 2 independent experiments. For Fig E2, C-E, G, and H, n = 10 mice per group combined from 2 independent experiments. For Fig E2, F, n = 5 mice per group representative of 2 independent experiments. *P < .05, **P < .01, and ***P < .001, unpaired t test (Fig E2, C-H) or 2-way ANOVA (Fig E2, A and B). n.s., Not significant. The dashed line is the limit of detection of the assay. Eos, Eosinophils; Lym, lymphocytes; Mφ, macrophages; Neu, neutrophils.