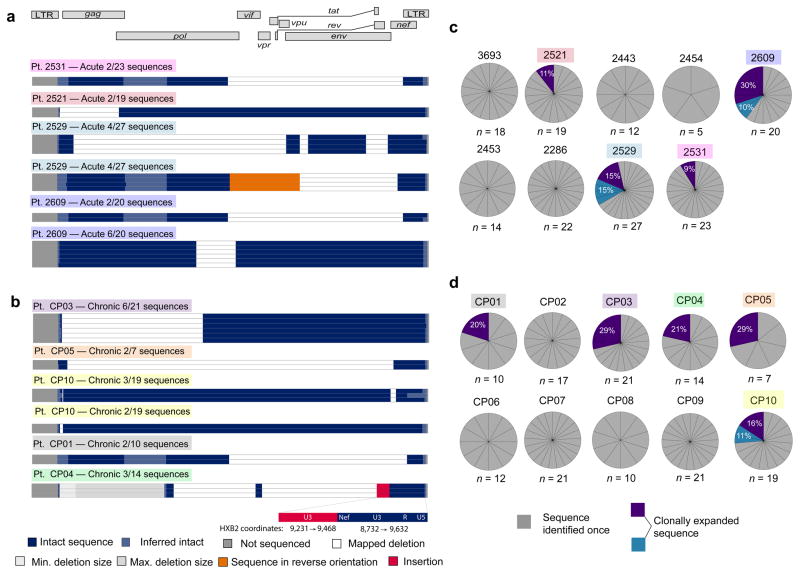
Figure 3.
Expanded clones identified in chronically and acutely treated subjects are grossly defective. (a,b) Maps of expanded HIV-1 clones identified in resting CD4+ T cells from subjects treated in acute (a) or chronic (b) infection. Expanded clones are defined as clones amplified in completely independent PCR reactions from a single subject that are identical at every nucleotide. The frequency of each clone is shown relative to the total number of clones identified in that subject. Colored boxes denote the subject in which each expanded clone was identified (see c,d) (c,d) Proportion of sequences from subjects treated during acute (c) or chronic (d) infection that are expanded clones. The number of sequences examined for each subject (n) is noted. Expanded clones (purple/blue) are shown as a percentage of total sequences from the relevant subject.