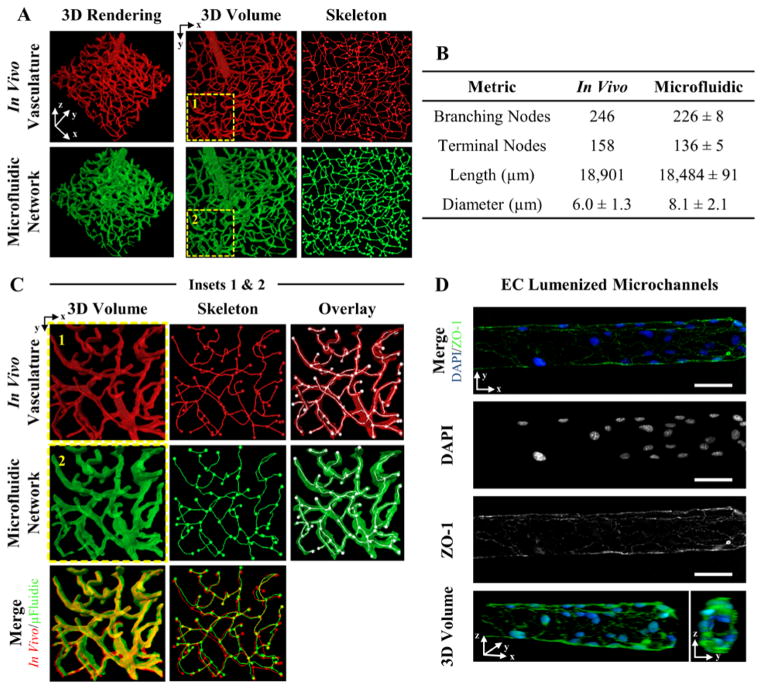
Figure 3. 3D Vascular -Derived Microfluidic Networks.
(A) A confocal image stack of (red) cerebral cortex vasculature was used to fabricate a (green) biomimetic microfluidic network in a PEGDA hydrogel. The in vivo and in vitro microfluidic networks were skeletonized for quantitative analysis. (B) Four metrics were used to quantity the microfluidic networks. (C) The insets in (A) are expanded to demonstrate the ability to recapitulate the dense, tortuous in vivo vascular network in PEGDA. (D) Microchannels were seeded with mouse brain endothelial cells, fluorescently labeled with DAPI (blue: nucleus) and ZO-1 (green: tight junctions), and imaged via confocal microscopy. (D) SB=50 μm.