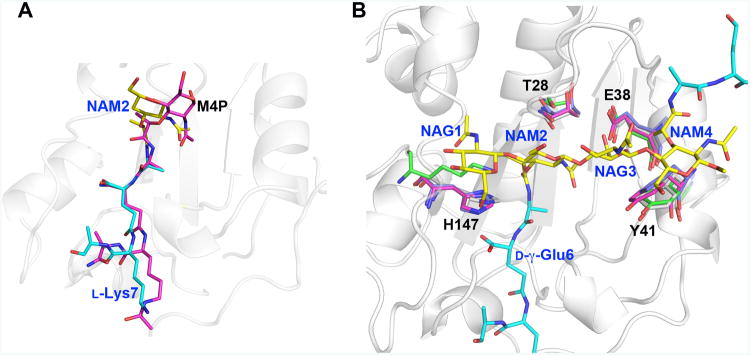
Figure 6. Key LytA residues essential for saccharide binding are structurally conserved in Gram-positive Firmicute amidases.
A. At first sight, the substrate peptide stems of M4P and di(GM5P) bind similarly to AmiA and LytA, respectively. However, while residues 2-4 of the peptide stem (d-iGln-l-Lys) in M4P align well with the corresponding residues in di(GM5P), with a displacement of 0.6-1.2Å, the position of l-Ala5 and the N-acetyl muramic acid NAM2 differ between 2.3-4.0 Å. Thus the central N-acetyl muramic acid in the AmiA/M-4P complex, corresponding to NAM2 in the LytA/di(GM5P) structure is positioned differently.
B. Structural alignment of the amidases AmiA, AmiE and PlyL in violet, magenta and green, respectively, on LytA in grey demonstrates that the position and conformation of the key residues Thr28, Glu38, Tyr41 and His147 are conserved except that a lysine residue replaces His147 in the bacteriophage amidase PlyL. Glycan moieties and peptide stems of the di(GM5P) substrate are in yellow and cyan, respectively.