Figure 3. Inhibition of NGF-dependent TrkA signaling by 1NMPP1.
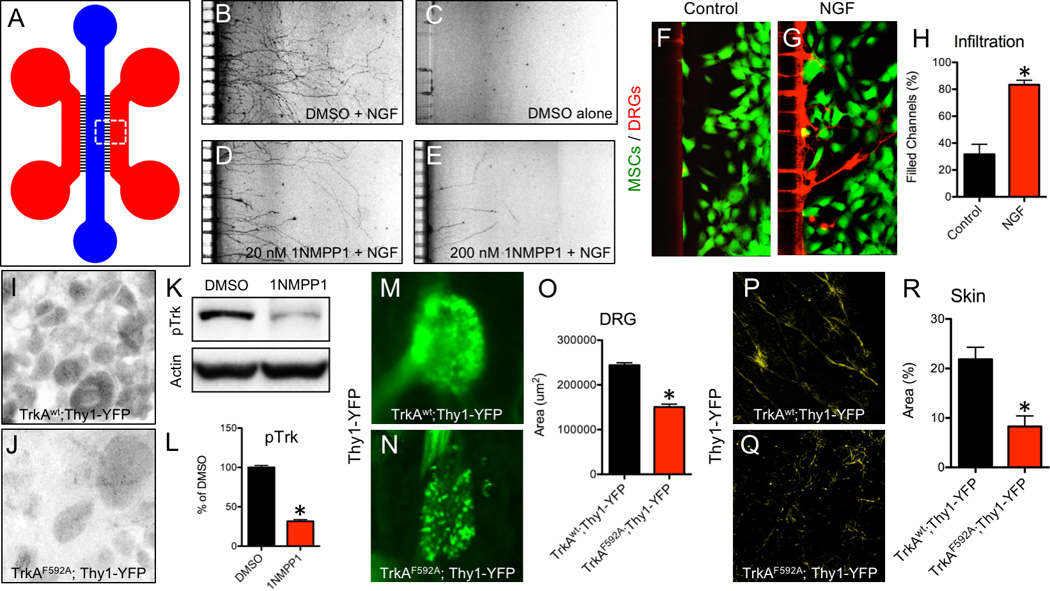
A) A microfluidic device was used to culture DRG neurons plated in the blue compartment to project axons through microchannels (3 µm H × 10 µm W) into the red compartment for visualization. Neuron outgrowth was visualized in B) Positive Control (DMSO + NGF), C) Negative Control (DMSO alone), D) Low Dose (20 nM 1NMPP1 + NGF), and E) High Dose (200 nM 1NMPP1 + NGF) cultures. MSCs were transfected with F) control or G) NGF cDNA and plated in the red compartment using media with suboptimal NGF, with H) axon infiltration quantification. DRGs were sectioned and stained with antibodies against pTrk in I) TrkAwt;Thy1-YFP and J) TrkAF592A;Thy1-YFP adult mice 24 hours after 1NMPP1 administration. K) Western blot against pTrk with loading control on protein extracted from DRGs of adult TrkAF592A;Thy1-YFP mice injected with DMSO or 1NMPP1 with L) quantification. Whole mount fluorescence imaging of intact DRGs at postnatal day 7 from M) TrkAwt;Thy1-YFP and N) TrkAF592A;Thy1-YFP littermates treated with 1NMPP1 during gestation with L) quantification. Whole mount fluorescence imaging of skin at postnatal day 7 from P) TrkAwt;Thy1-YFP and Q) TrkAF592A;Thy1-YFP littermates treated with 1NMPP1 during gestation with R) quantification. * p < 0.05 by unpaired Student’s t-test.
