Figure 3. Hemophagocytic histiocytosis characteristics.
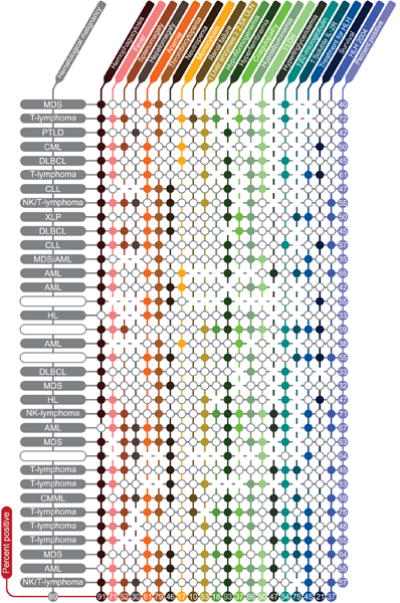
Each closed circle (○) represents a negative result. Blanks represent missing information. Each row is one patient and each column is a variable. Numbers show percent positive patients (for each characteristic) or percent positive characteristics (for each patient) excluding missing information. Variables evaluated (listed in order of columns) included BM/lymph node/spleen hemophagocytosis per pathology evaluation, fever, splenomegaly (clinically palpable spleen), hepatomegaly (clinically palpable liver), anemia (hemoglobin < 9.0 g/L), thrombocytopenia (platelets < 100 × 109/L), neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count (ANC) < 1.0 × 109/L), monocytosis (absolute monocyte count (AMC) > 1.0 × 109/L), renal failure (≥ 50% increase in creatinine over baseline), elevation of hepatic enzymes (≥ 2.5× upper limit of normal), hypofibrinogenemia (fibrinogen ≤ 150mg/dL), hyperferritinemia (ferritin ≥ 500micrograms/L), coagulopathy (PT ≥ 1.5× upper limit of normal and/or PTT ≥ 1.5× upper limit of normal and/or D-dimer ≥ 10.0mcg/mL), hypoalbuminemia (< 3.5g/dL), elevated LDH (≥ 2.5× upper limit of normal), hypertriglyceridemia (≥ 265 mg/dL), elevated b2-microglobulin (≥ 2mg/L), and elevated soluble IL-2 receptor (CD25) ≥ 2400U/mL. Abbreviations: Hb, hemoglobin; ULN, upper limit of normal; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; HLH 2004, Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis 2004 diagnostic criteria; MDS, myelodysplastic syndromes; PTLD, post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder; CML, chronic myeloid leukemia; DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; XLP, X-linked lymphoproliferative disease; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; HL, Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
