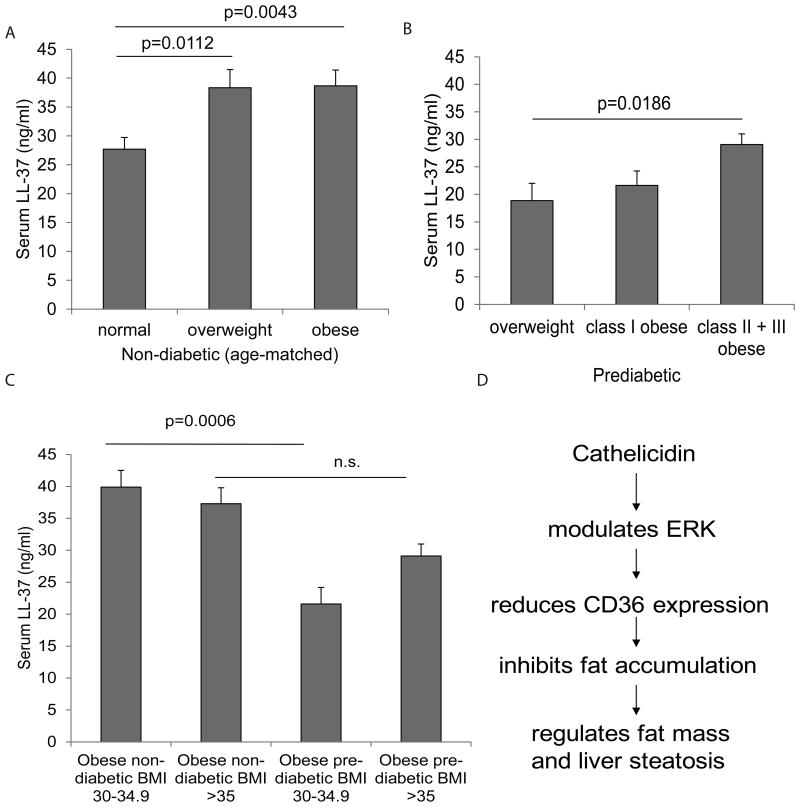
Figure 6. Circulating cathelicidin LL-37 levels are positively correlated with BMI of non-diabetic subjects.
(A) The age-matched data pool of non-diabetic subjects is divided into 3 groups according to CDC BMI-obesity definitions (normal BMI<24.9 n=11; overweight BMI 25.0-29.9 n=12; obese BMI>30 n=11). The serum LL-37 levels of obese non-diabetic patients are significantly higher than those of normal non-diabetic subjects. (B) The data pool of prediabetic patients is divided into 3 groups according to CDC BMI-obesity definitions (overweight BMI<25-29.9 n=5; class I BMI 30-34.9 n=10; class II + III obese BMI>35 n=5). Class II obese and III obese prediabetic patients have significantly higher serum cathelicidin levels than overweight prediabetic patients. (C) The LL-37 levels of the non-diabetic and prediabetic groups. Circulating LL-37 levels of prediabetic groups with BMI range 30-34.9 are significantly lower than those of non-diabetic subjects with the same BMI range. LL-37 levels of prediabetic patients and non-diabetic subjects with BMI >35 are similar. Non-diabetic BMI 30-34.9 n=17; non-diabetic BMI >35 n=16; prediabetic BMI 30-34.9 n=10; prediabetic BMI >35 n=5. (D) Summary of cathelicidin-mediated effects.