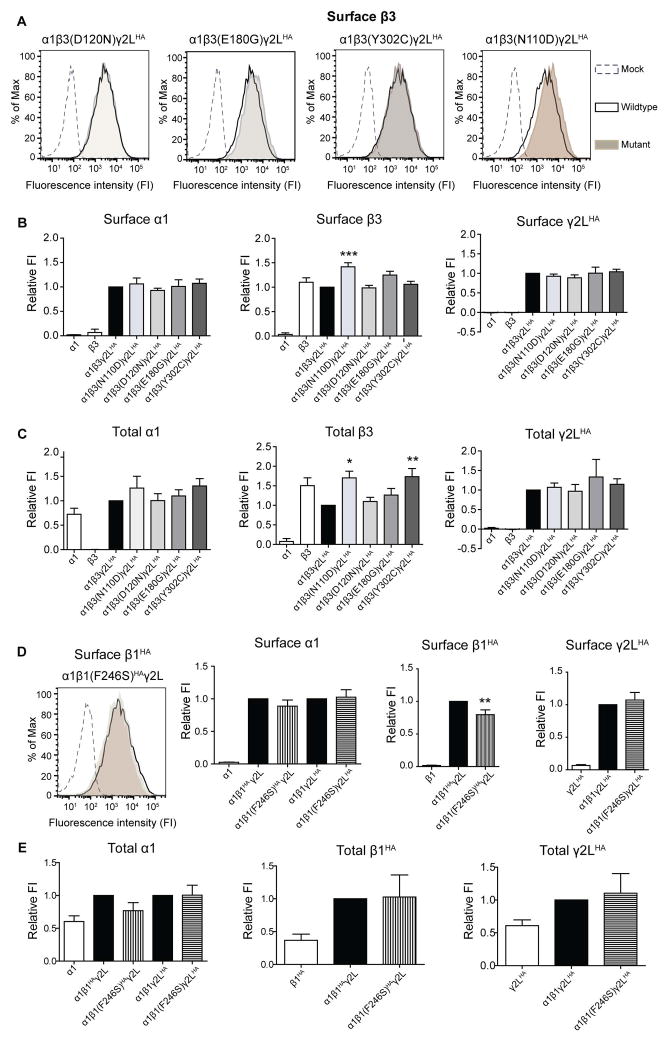
Figure 4. The β subunit mutations did not reduce surface and total levels of GABAA receptor subunits.
Flow cytometry was used to determine surface (A, B, D) and total (C, E) levels of α1, β1HA/ β3 and γ2LHA subunits in HEK293T cells. (A, D left most panel) Representative fluorescence intensity (FI) histograms showing the surface β3/β1HA subunit levels from cells expressing α1mutant β3/β1HAγ2L subunits (shaded), α1wt β3/β1HAγ2L subunits (unfilled with solid black line) and empty vector (unfilled with black line). The bar graphs represent FI of the Alexa 674 fluorophore for each condition normalized to the intensity of the wt condition (Relative FI). Surface (B,D) and total (C,E) relative FI levels of α1, β3/β1HA and γ2LHA subunits in cells expressing only α1, β3/β1HA or γ2LHA subunits (used as antibody controls), as well as co-expressing α1, γ2LHA, wt or mutant β3/β1HA subunits (hom condition). In the hom condition the IS-associated β3(N110D) and LGS-associated β3(E180G) subunit mutant subunits had 42 % and 25 % higher surface levels, respectively, than β3 subunits in the wt condition. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test was used to determine significance. * represents significant difference compared to the wt condition, * = p<0.05, ** = p<0.001, *** = p<0.0001. (A) and (D) share same legends.