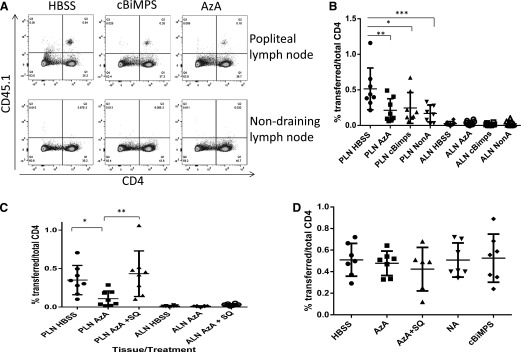
Figure 6. T cell tissue egress is inhibited following treatment with odorants.
(A and B) Purified CD45.1+ congenic CD4+ T cells from naïve mice were examined for their capacity to exit the footpad over 16 h following pretreatment with 5 mM AzA, 50 μM cBiMPS, or diluent. Representative FACS plots are shown in A, with combined data shown in B. (B) Means ± sd represent 4 separate experiments, each using T cells pooled from ≥3 mice. In parallel, cells were treated with SQ22538 (SQ) or diluent before pretreatment with AzA or diluent (C) and examined for their capacity to exit the footpad over 16 h. (C) Means ± sd represent 4 separate experiments, each using T cells pooled from ≥3 mice. (D) Additionally, in parallel, cells were treated as for A and C and then injected intravenously. Spleen cells were examined for transferred cell number and viability after 16 h. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. PLN, popliteal lymph node; ALN, axillary lymph node.