Figure 1.
P. berghei Hepatic Infection Alters the AMPK Activation Status
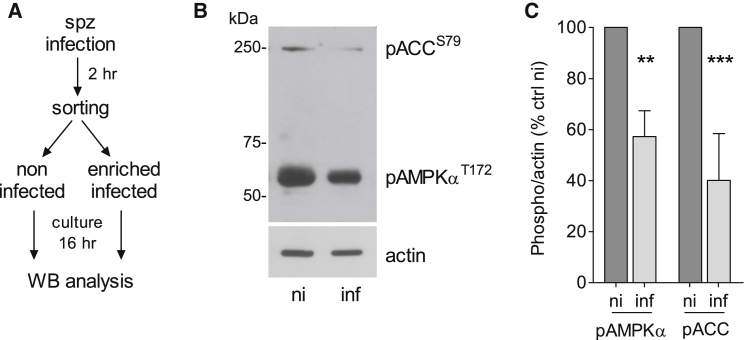
(A) Timeline of infection and sample collection. Huh7 cells were infected with GFP-expressing P. berghei sporozoites (spz) and subjected to fluorescence-activated cell sorting to separate infected from non-infected (ni) cells at 2 hr post-infection. Cells were re-plated 1:1 (infected:non-infected), cultured for 16 hr, and compared to non-infected by western blot (WB).
(B and C) WB analysis of lysates from non-infected (ni) and enriched infected (inf) Huh7 cells collected at 18 hr post-infection, probing with anti-phospho-AMPKα (pAMPKαT172), -phospho-ACC (pACCS79), and -actin antibodies. (B) Representative blot and (C) quantitative analysis (mean ± SEM) of three independent experiments. Analysis of additional time points and control (ctrl) for total AMPKα abundance is shown in Figure S1. ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.