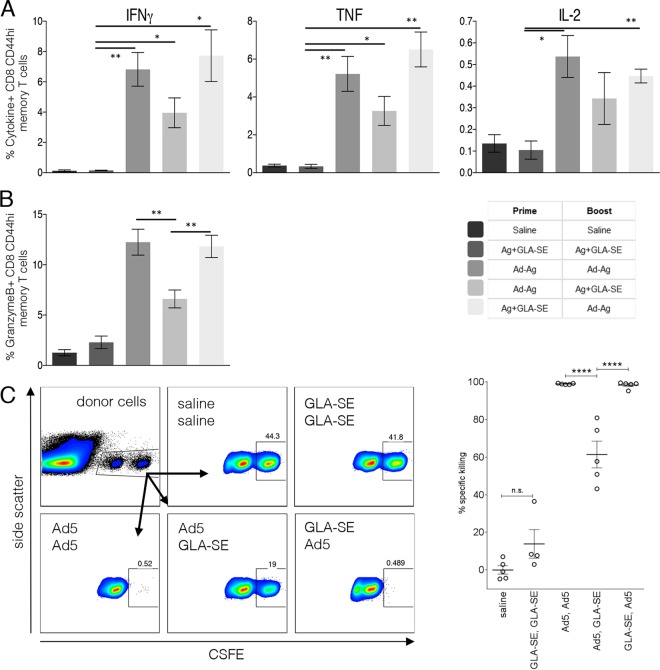
FIG 2.
Immunization regimens that include an Ad5-based vaccine generate memory CD8 T cells. C57BL/6 mice were primed, and 6 weeks later boosted, with the indicated vaccines. Sixteen weeks after the boost, spleens were removed and single-cell suspensions prepared. Cells were incubated with F3 MHC-I peptides and analyzed by flow cytometry for expression of the indicated cytokine (A) or granzyme B (B). To determine killing by CD8 memory T cells, control and peptide-pulsed spleen cells from untreated mice were stained with a low (0.2 μM) or high (2 μM) concentration of CFSE and mixed at a 1:1 ratio (donor cells) (C). Donor cells were injected intravenously into immunized mice and, 18 h later, recovered from the spleens. Data are representative flow cytometry plots, with the previous immunization regimen indicated, and specific killing as determined by contrasting the ratio of control and peptide-pulsed cells recovered. Data are means and SEM (n = 5 per group) and are representative of results obtained in 2 or 3 independent experiments. * and **, P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively, for the indicated groups. In panels A and B, with the exception of Ag+GLA-SE/Ag+GLA-SE, immunization-induced responses were significantly greater (P < 0.05) than those observed following saline/saline injection. n.s., not significant.