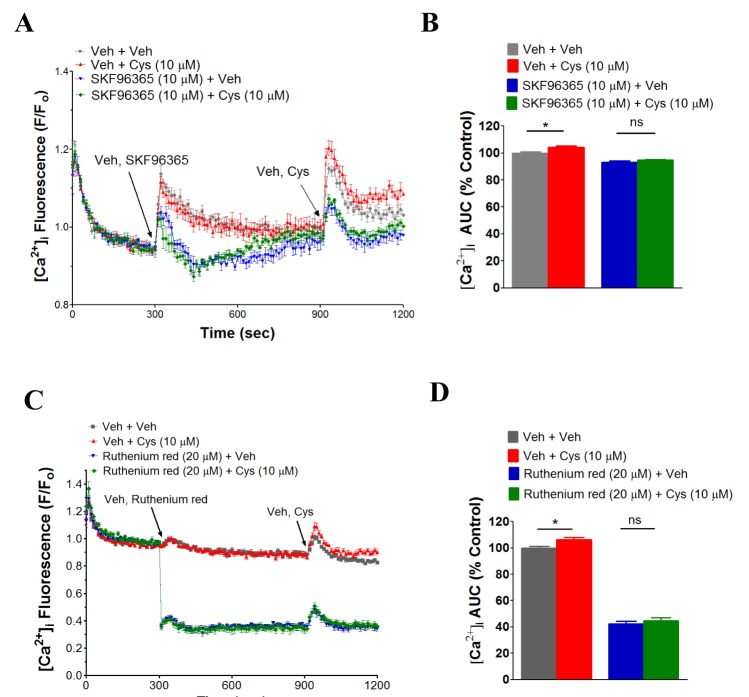
Fig. 5. SKF96365 and ruthenium red inhibit cysteine-induced [Ca2+]i increase in human neutrophils.
Ca2+-channel inhibitors (A) SKF96365 (10 µM) and (C) ruthenium red (20 µM), and cysteine (10 µM) were added at the time points indicated by the arrowheads. [Ca2+]i was measured as described in methods and materials. Changes in [Ca2+]i were expressed as the relative fluorescence intensity of Fluo-3 AM over baseline fluorescence intensity (F/F0). (B, D) [Ca2+]i following addition of Ca2+ channel inhibitors were indicated as area under curve (AUC), which was calculated for 300 s (900~1200 s) and was expressed as percentage control (% control). Data were analyzed by Graphpad Prism 5.0 (Graphpad software) using ANOVA. Bonferroni test was used for post-hoc comparison. An average of three independent experiments is shown. ns, no significant difference, *p<0.05.