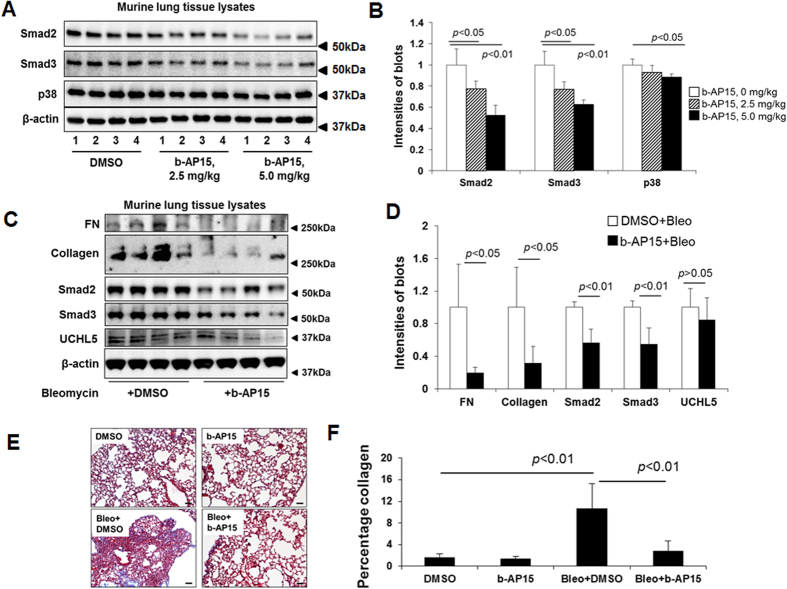
Figure 7. Administration of b-AP15 reduces bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice.
(A) C57BL/6 mice were intraperitoneally injected with b-AP15 (2.5 mg/kg or 5.0 mg/kg, 3 × 1 every other day) for 8 days, and then lung tissues were collected. Lysates from lung tissues were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies to Smad2, Smad3, p38, and β-actin. (B) Intensities of blots in the A were quantified by imageJ software. (C) C57BL/6 mice were intranasally challenged with bleomycin (0.045 U/mice). Starting from day 11, mice were intraperitoneally injected with DMSO (0.25%) or b-AP15 (5.0 mg/kg in DMSO) 4 times of every other day. At day 21, lung tissues were collected and lysates from lung tissues were analyzed by immunoblotting with FN, type I collagen, Smad2, Smad3, UCHL5, and β-actin antibodies. Western blot images were cropped to improve the conciseness of the data; samples derived from the same experiment and the blots were processed in parallel. (D) Intensities of blots in the (C) were quantified by imageJ software. (E) The right lungs were fixed with 3.7% formaldehyde. Masson’s trichrome staining was performed to detect the collagen in the marine lung slices. (F) The percentages of collagen deposition in the E were analyzed by NIS-Elements software.