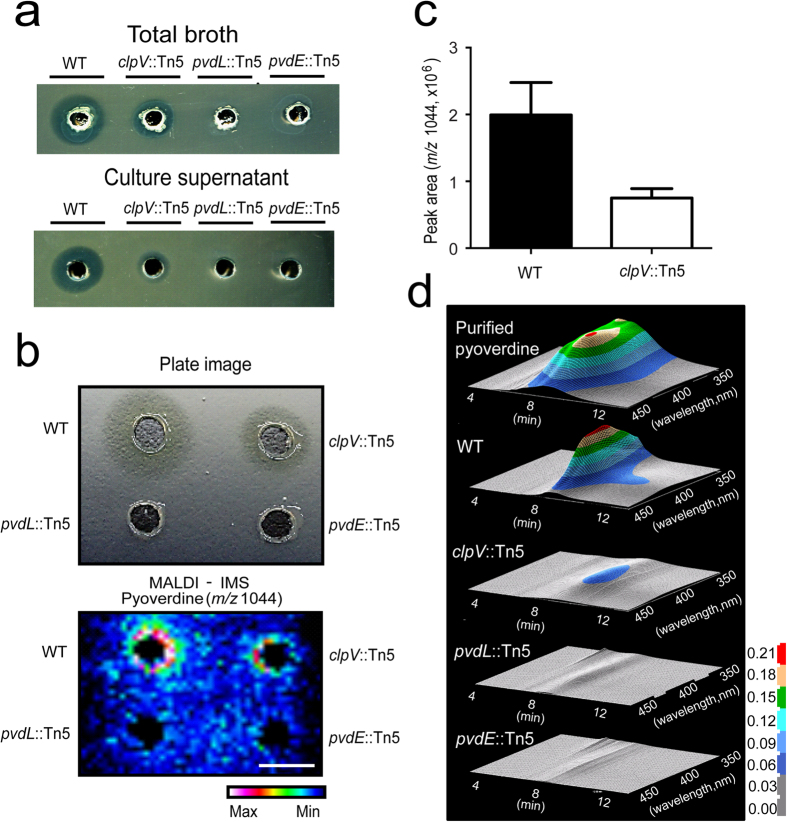
Figure 2. Characterization of the pyoverdine secretion system.
(a) Zone of inhibition assay for anti-Xoo activity was tested in 1/2 TSB medium which contained Xoo. Whole culture (top a) and cell-free culture supernatant of WT, clpV::Tn5, pvdL::Tn5, and pvdE::Tn5, which were collected after incubation for 24 h in LP media, were injected into the hole to test toxicity against Xoo (bottom a). (b) MALDI-IMS imaging of pyoverdine from incubation of wild-type and mutant P. taiwanensis with Xoo. Competition plates of P. taiwanensis and mutants co-cultured with Xoo for IMS (top b). The MALDI-IMS image shows an ion of m/z 1044 [M + H]+, displaying the highest level surrounding the hole between the wild-type and mutant treatment (bottom b). Scale bar, 2 mm. Intensity gradients for pyoverdine are illustrated by color histograms (maximum, white; minimum, black). (c) LC-MS quantification of pyoverdine in cell free culture supernatants of WT and clpV::Tn5 after 24-h incubation in iron-limited media. (d) HPLC quantification of pyoverdine (m/z 1044) and culture supernatant from wild-type and mutants. Fluorescent pyoverdine was monitored at 400 nm under the UV detector. Pyoverdine was purified using Cu-sepharose.