Figure 1.
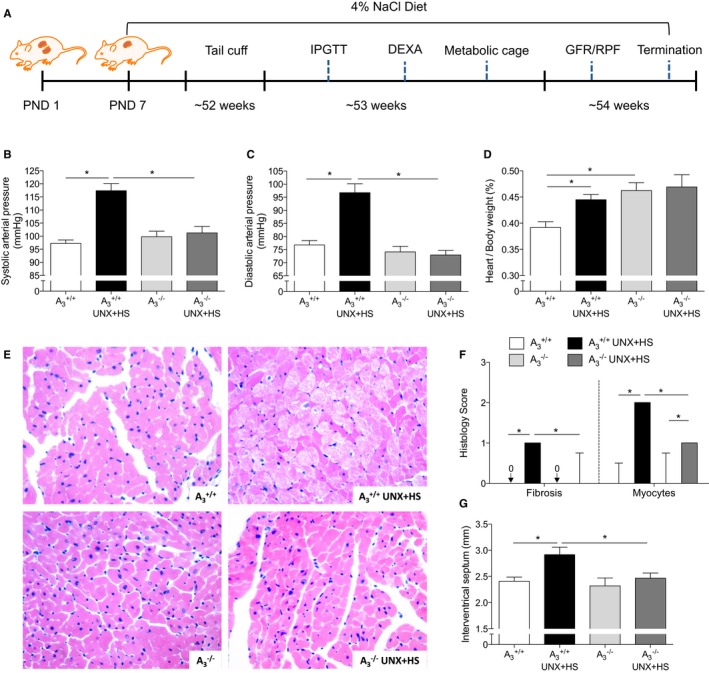
Blood pressure and heart histology. A, The protocol and timeline of experiments. UNX in combination with HS (UNX‐HS) significantly increased the systolic and diastolic arterial pressure in A3 +/+ but not in A3 −/− mice (B and C). 2×2 ANOVA revealed significant (P<0.0001) interaction (ie, effects of genotype on the response to UNX‐HS). UNX‐HS also increased the heart/body weight ratio in A3 +/+ mice; the A3 −/− mice had a higher baseline heart/body weight ratio compared with A3 +/+ mice but were not affected by UNX‐HS (D). Representative pictures of hematoxylin and eosin staining in the heart are shown in (E). The A3 +/+ mice showed significantly worse pathological changes in the heart following UNX‐HS, which was evaluated as fibrosis and myocyte histological scores (F). The thickness of the intraventricular septum was significantly increased in the A3 +/+ mice after UNX‐HS, but there were no changes in the A3 −/− group (G). Data are shown as mean±SEM, except in (F), in which results are presented as median and interquartile range. *P<0.05, n=8 to 12 per group. DEXA indicates dual‐emission x‐ray absorptiometry; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; HS, high salt; IPGTT, intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test; PND, postnatal day; RPF, renal plasma flow; UNX, uninephrectomy.
