Figure 4.
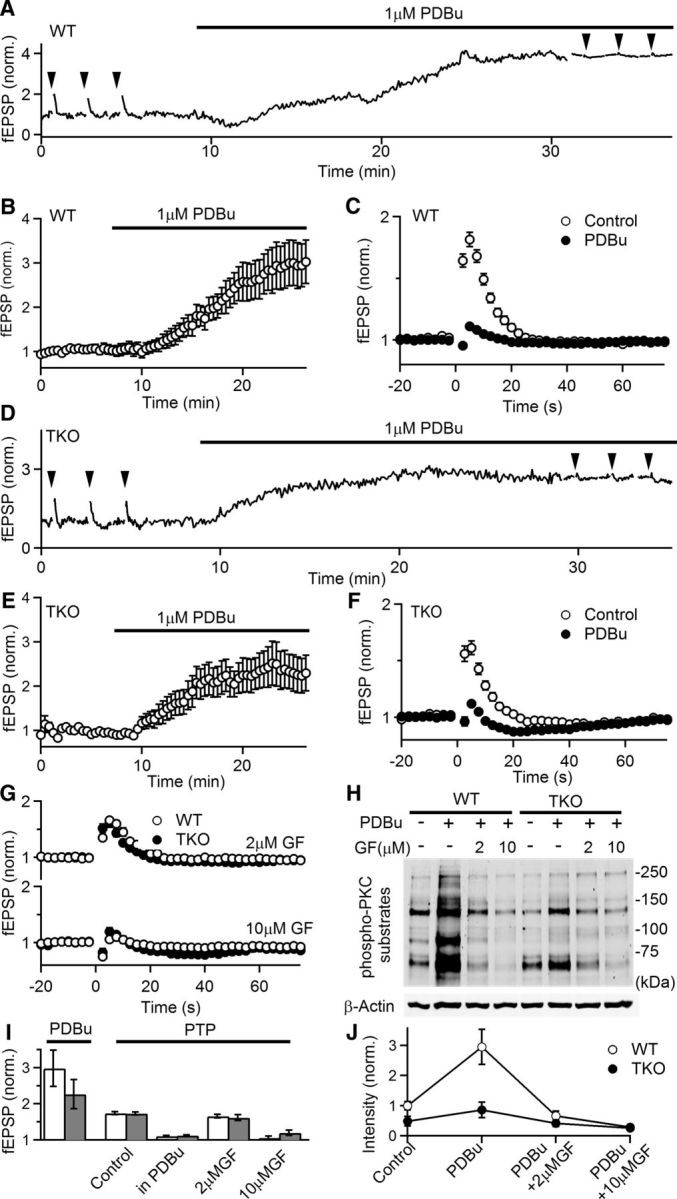
The phorbol ester PDBu enhances synaptic responses and occludes PTP in both WT and TKO animals. A, Representative experiment showing normalized fEPSPs as a function of time in a WT slice. fEPSPs were recorded in 1.5 mm external Ca2+ and PTP (50 stimuli at 50 Hz induction) was monitored before and after the application of the PKC activator PDBu (1 μm). Induction of PTP is indicated by arrowheads. B, Average normalized fEPSPs during PDBu application in WT animals (n = 17, 7). fEPSPs were recorded every 5 s to monitor the effects of PDBu but displayed in the plot every 25 s for clarity. C, Comparison of PTP before and after the application of PDBu in WT slices. D–F, Similar to A–C, but in TKO animals (n = 13, 4). G, PTP (50 stimuli at 50 Hz induction) in the presence of the indicated concentrations of the PKC inhibitor GF in WT (open symbols) and TKO (filled symbols) animals. (WT control: n = 42, 15; WT + 2 μm GF: n = 10, 2; WT + 10 μm GF: n = 8, 2; TKO control: n = 29, 11; TKO + 2 μm GF: n = 7, 2; TKO + 10 μm GF: n = 8, 2). H, Protein analysis of phosphorylated levels of PKC substrates in the presence of PKC activator PDBu (1 μm) with and without the preincubation in the indicated concentrations of GF for 1 h. I, Summary of physiology experiments. Empty bars: WT; filled bars: TKO. J, Quantification of phosphorylated levels of PKC substrates in H. Intensity is normalized to WT control conditions (n = 5 for both genotypes).
