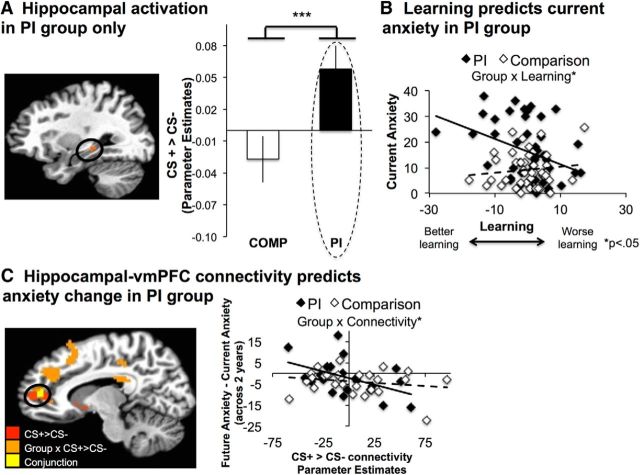
Figure 3.
Hippocampal activation and connectivity. A, PI youth recruited the hippocampus more strongly for CS+ trials than for CS− trials relative to comparisons, p < 0.05 FWE corrected. B, Learning (adjusted for age and sex) correlated with current anxiety for PI youth. C, Hippocampal–vmPFC connectivity was identified by the main effect of condition (CS+ > CS−; shown in red) and by the condition × for PI youth group interaction condition (shown in orange). Overlap between the two analyses is shown in yellow. Hippocampal–vmPFC connectivity in the vmPFC cluster identified by the main effect of condition (adjusted for age, sex, and baseline anxiety) predicted a significant decrease in anxiety symptoms 2 years later. All error bars reflect between-subjects SE.