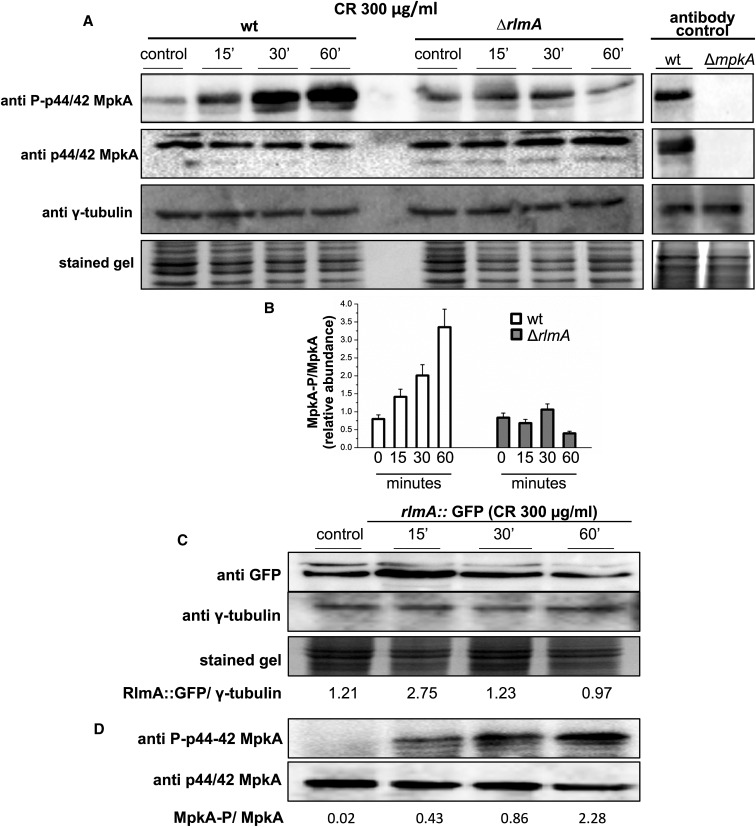
Figure 6.
The ΔrlmA mutant strain has impaired CWI pathway activation. (A) Conidia from the wild-type and mutant strain were grown for 16 hr in liquid medium and cell wall stress was induced through exposure to CR for 0, 15, 30, and 60 min. The phosphorylated fractions and the total MpkA amount were detected using anti-phospho p44/42 MAPK and anti-p44/42 MAPK antibodies, respectively. No detection is observed in the ΔmpkA mutant (antibody control). The γ-tubulin antibody and the Coomassie Brilliant Blue stained gel were used as loading sample controls (A). Densitometry analysis of western blots showing the ratio of phosphorylated MpkA/nonphosphorylated MpkA in the wild-type and ΔrlmA mutant strain expressed as the relative abundance (B). The conidia of the rlmA::gfp strain were cultured under the same conditions as those described in (A). Protein extracts from different time points were subjected to western blots to detect the total amount of RlmA using anti-GFP antibodies. Signal intensities were quantified as the RlmA::GFP/γ-tubulin pixel intensity ratio (C). The rlmA::gfp strain was cultured under the same conditions as those described in (C) and subjected to western blot analysis to detect both the phosphorylated fraction and the total MpkA protein as described in (A). CR, congo red; CWI, cell wall integrity; GFP, green fluorescent protein; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; wt, wild-type.