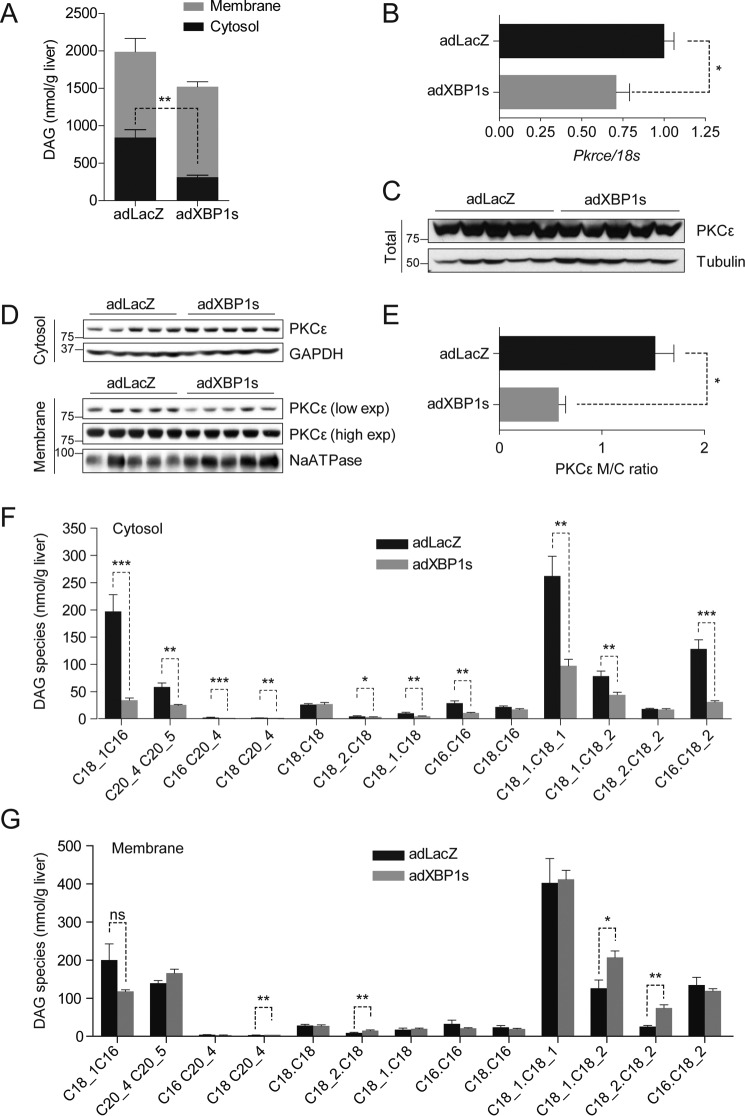
FIGURE 2.
XBP1s reduces hepatic diacylglycerol content and PKCϵ activity. C57Bl6/J mice were fed an HFD (45% kcal) for 12 weeks (starting at 3 weeks of age) and injected with adLacZ or adXBP1s (8*10E7 pfu/g) through the tail vein. A, DAG content was determined in in cytosolic (black columns) and membrane (gray columns) compartments in livers of 6 h-fasted mice on post-injection day 9. Total DAG content was calculated from the sum of cytosolic and membrane DAG content. B, relative mRNA levels of Pkrce. Gene expression was normalized using the 18s gene as a housekeeping gene. C, Western blotting analysis of PKCϵ protein in whole liver homogenates. Tubulin was used as a loading control. D, PKCϵ protein levels were determined in the cytosol (top panel) and membrane (bottom panel) compartments of livers of 6 h-fasted mice 9 days post-injection. GAPDH was used as a loading control for cytosolic lysate, whereas NaATPase served as a loading control for the membrane lysates. E, PKCϵ protein expression was quantified using densitometric analysis of the autoradiographical signal of PKCϵ in the membrane and cytosol. The membrane-to-cytosol (M/C) ratio as measure of PKCϵ activity is expressed in the graph. Hepatic DAG species were analyzed in the cytosol (F) and membrane (G) compartments of livers of adLacZ- and adXBP1s-expressing mice. Error bars are represented as mean ± S.E.; p values were determined by Student's t test. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ns, not significant.