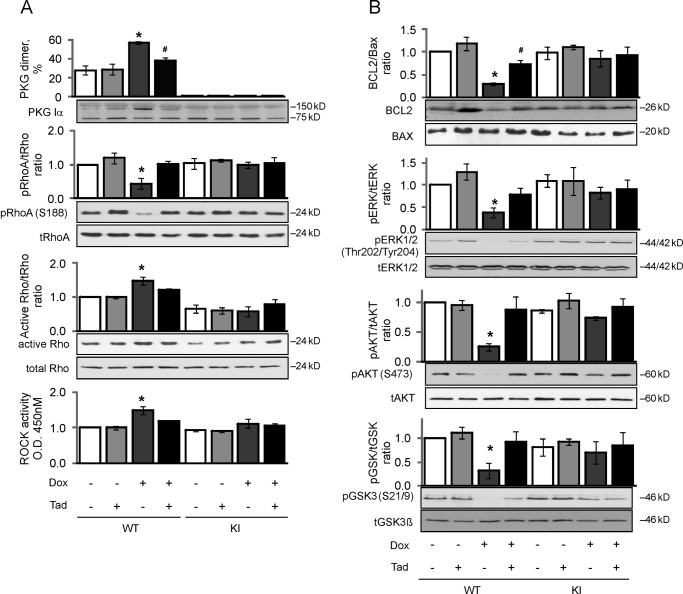
FIGURE 5.
Tadalafil limits doxorubicin-induced PKG Iα oxidation and the associated apoptotic signaling in WT, whereas KI are basally protected. A, PKG Iα disulfide dimerization, RhoA Ser-188 phosphorylation, RhoA, and ROCK activity in WT or KI hearts treated with doxorubicin (Dox) or vehicle, in the presence or absence of tadalafil (Tad), was indexed (n = 4). This demonstrated that doxorubicin triggered a loss of pro-survival phospho-RhoA (Ser-188) signaling in WT, and this was attenuated by PDE5 inhibition with tadalafil. B, BCL2/Bax ratio, ERK, AKT, and GSK3β phosphorylation in hearts from WT or KI mice treated with doxorubicin or vehicle, in the presence or absence of tadalafil, was indexed. Consistent with the loss in anti-apoptotic phospho-RhoA induced by doxorubicin in WT hearts, there was a concomitant loss of pro-survival signaling in terms of BCL2/Bax ratio, ERK, AKT, and GSK3β. *, p < 0.05 between vehicle and DOX groups; #, p < 0.05 between DOX alone and DOX + tadalafil groups.