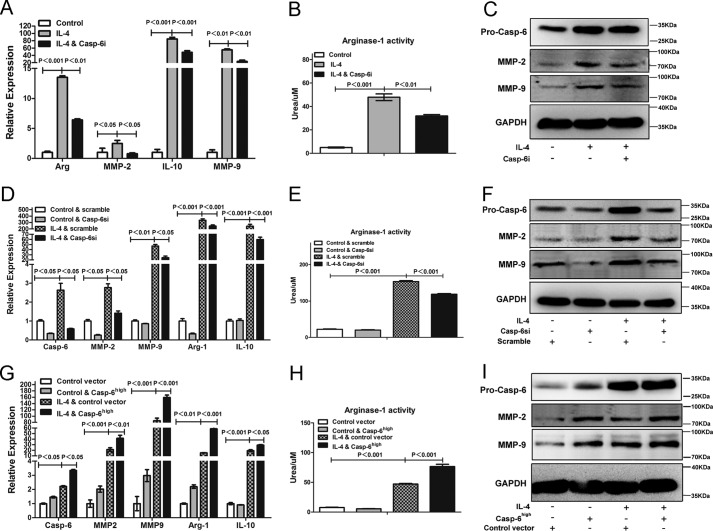
FIGURE 5.
Caspase-6 is a regulator during alternative activation of macrophages. A–C, RAW264.7 cells were treated with or without Caspase-6-specific inhibitor (Casp-6i) in the presence of stimulus of IL-4 (10 ng/ml) for 24 h. A, Casp-6i could strikingly reduce the expression of Arginase-1, IL-10, MMP-2, and MMP-9 induced by IL-4. B, Casp-6i inhibited IL-4-induced arginase-1 activity of RAW264.7 cells. C, Western blotting analysis showed that the protein levels of MMP-2 and MMP-9 were significantly inhibited by Casp-6i. D–F, RAW264.7 cells were transfected with scramble siRNA or siRNA against caspase-6 (Casp-6si) prior to stimulus of IL-4 (10 ng/ml) for 24 h. D, Casp-6si could significantly reduce the expression of arginase-1, IL-10, MMP-2, and MMP-9 induced by IL-4, compared with scramble siRNA. E, Casp-6si inhibited IL-4-induced Arginase-1 activity of RAW264.7 cells, compared with scramble siRNA. F, Western blotting analysis showed that the protein levels of MMP-2 and MMP-9 were also inhibited by Casp-6si. G–I, RAW264.7 cells were transfected with control vector or caspase-6 overexpressed vector (Casp-6high) prior to stimulus of IL-4 (10 ng/ml) for 24 h. G, Casp-6high macrophages greatly increased the expression of arginase-1, IL-10, MMP-2, and MMP-9 induced by IL-4, compared with macrophages that transfected with control vector. H, Casp-6high macrophages promoted IL-4-induced Arginase-1 activity of RAW264.7 cells compared with macrophages that transfected with control vector. I, Western blotting analysis showed that the protein levels of MMP-2 and MMP-9 were markedly increased in Casp-6high macrophages. Values were expressed as means ± S.D. (p values of plotted data of ≤0.05 were considered statistically significant).