FIGURE 4.
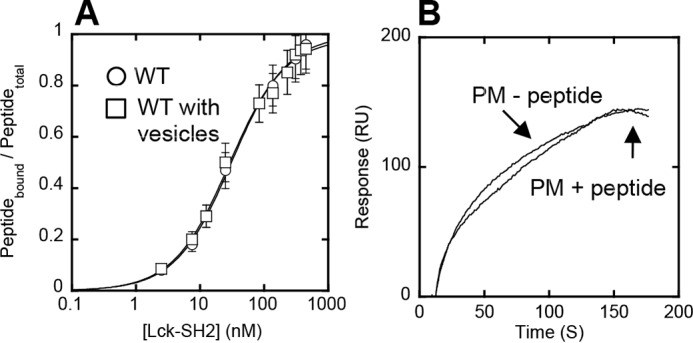
Orthogonal functionality of lipid and peptide binding sites of Lck-SH2. A, binding of Lck-SH2 to the Tyr(P) peptide (pYEEI) monitored by fluorescence anisotropy in the presence (□) and absence (○) of 40 μm PM mimetic vesicles. The peptide concentration was 50 nm. Notice that vesicles have no effect on peptide binding of Lck-SH2. Data represent means ± S.D. from triplicate measurements. B, effect of the Tyr(P) peptide on membrane binding of Lck-SH2. The SH2 domain was allowed to interact with the PM mimetic vesicles before and after a 30-min incubation with 100 μm peptide. The Lck-SH2 domain concentration was 50 nm. The peptide had a negligible effect on the membrane binding of Lck-SH2, showing the orthogonality of lipid and peptide binding. Sensorgrams are a representative from triplicate measurements that show essentially the same results.
