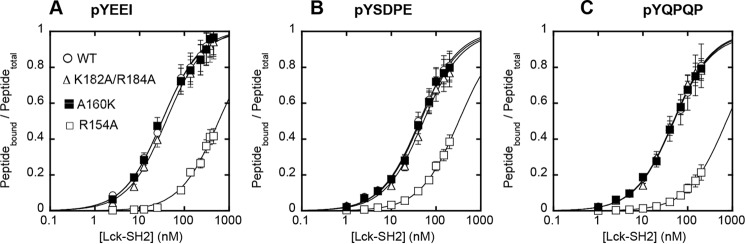
FIGURE 5.
Tyr(P) binding affinity of Lck-SH2 WT and mutants. Affinity of Lck-SH2 WT (○), R154A (Tyr(P) site mutant) (□), K182A/R184A (LOF lipid site mutant) (Δ), and A160K (GOF lipid site mutant) (■) for three different Tyr(P)-containing peptides, pYEEI (A), pYSDPE (B), and pYQPQP (C), that have been reported to specifically bind the Lck-SH2 was measured by fluorescence anisotropy analysis as described in Fig. 4. For all three peptides, Lck-SH2 WT (Kd = 33 ± 7 nm for pYEEI), K182A/K184A (Kd = 40 ± 8 nm for pYEEI), and A160K (Kd = 32 ± 3 nm for pYEEI) showed comparable affinity, whereas R154A (Kd = 570 ± 200 nm for pYEEI) exhibited a ≈20-fold decrease in affinity. The peptide concentrations used varied from 5 to 500 nm depending on the Kd values. Data represent means ± S.D. from triplicate measurements.