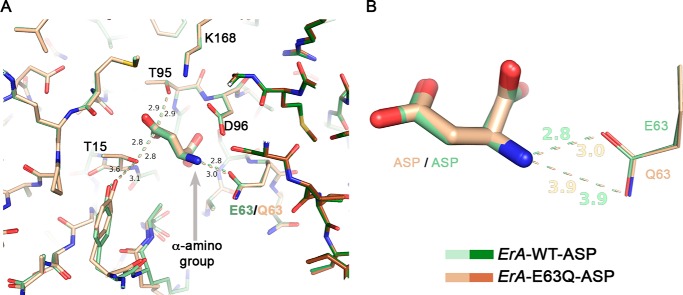
FIGURE 3.
The E63Q mutation has a minor effect on Asp binding. A, overlay of the ErA-WT·Asp (a region from two of the four protomers that build the tetramer are shown in pale and dark green) and the ErA-E63Q·Asp (beige and brown) structures. The structures are basically identical, with the most significant difference being an increased distance (3.0 versus 2.8 Å) between the side chain of residue 63 (Gln-63/Glu-63) and the α-amino group of Asp (gray arrow). B, zoom on the Asp-Glu-63/Gln-63 interaction. Both oxygen atoms of the Glu-63 side chain are compatible with a close distance to the α-amino group of Asp. In contrast, for Gln-63, the side chain amide nitrogen atom (H-bond donor) would not be compatible with proximity to the α-amino group of Asp (also an H-bond donor). This is not a factor when the ligand is Asp but becomes paramount for the larger amino acid Glu (also see section “Modeling the Glu Binding Mode to the Mutant ErA Variants”).