FIGURE 5.
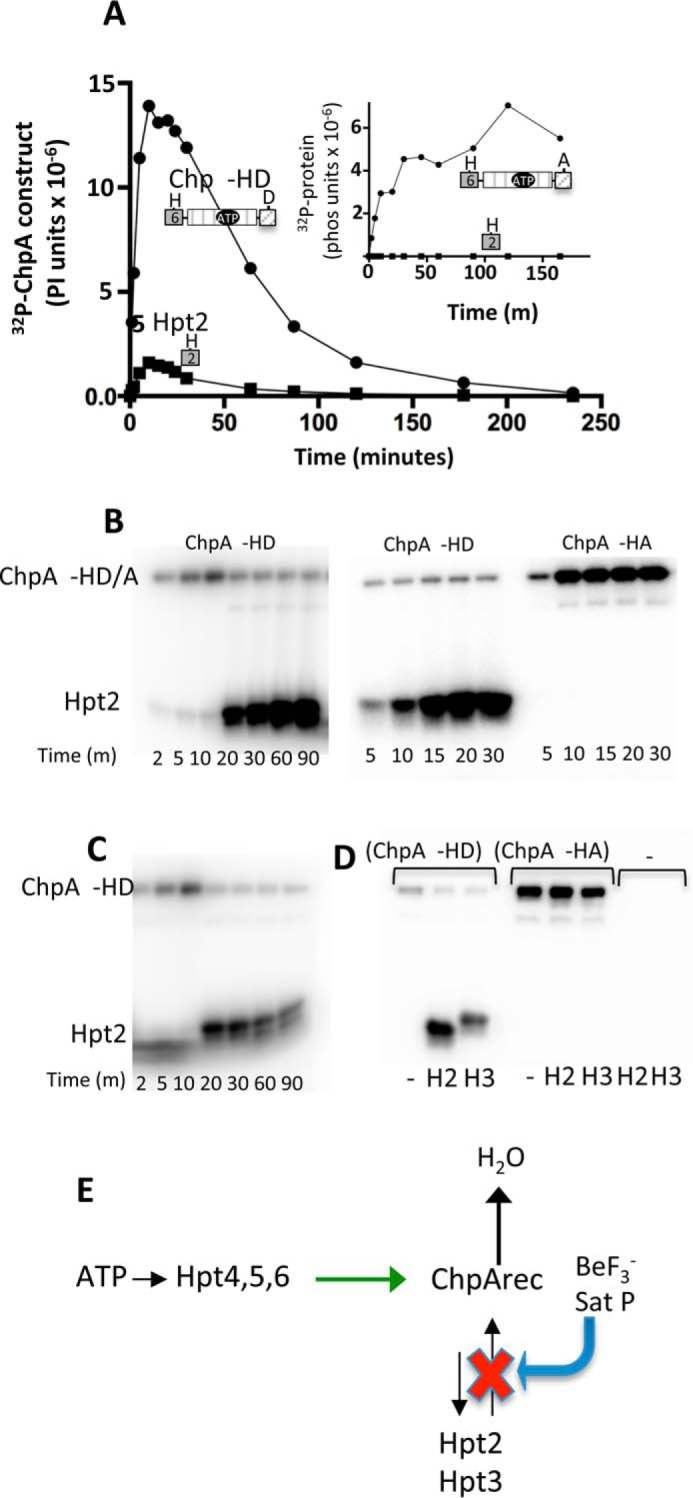
Reversible phosphotransfer between ChpArec and Hpt2/3. A, time courses for incorporation of 32P into ChpA −HD (closed circles) and His6-Hpt 2 (closed squares) in a reaction that contained 7.3 μm ChpA −HD and 34 μm Hpt2. The reaction was initiated by the addition of 30 μm [γ-32P]ATP. Aliquots were removed at the indicated times and analyzed by gel electrophoresis and phosphorimaging analysis. The inset shows results from the identical experiment except ChpA −HA was used instead of ChpA −HD. B, effect of excess BeF3− on the distribution of 32P-phosphoryl groups between ChpA −HD and Hpt2. In the left panel, the reactions were initiated as for A, and then 70 μm BeF3− (70 μm BeCl2 and 10 mm NaF) was added immediately after taking the 10-min time point. In the middle and right panels, 70 μm BeF3− was mixed with 34 μm untagged Hpt2 and 7.3 μm ChpA −HD (middle panel) or ChpA −HA (right panel). 30 μm [γ-32P]ATP was added to initiate the reactions, and the time points were removed at the indicated times. C, effect of addition of a swamp of unlabeled ATP on the distribution of 32P-phosphoryl groups between ChpA −HD and Hpt2. The reaction was carried out as in A except that 2 mm unlabeled ATP was added immediately after the 10-min time point. D, reactions contained 7.3 μm ChpA −HD, ChpA −HA, or no ChpA construct (−), 56 μm Hpt 2, Hpt3, or no Hpt (−), and 30 μm [γ-32P]ATP. After 10 min, 2 mm ATP was added and the reactions proceeded for 10 min before quenching and analysis. E, scheme summarizing reversible flow of phosphoryl groups between ChpArec and Hpt2,3. Binding BeF3− or saturating the phosphorylation sites of ChpArec inhibits Hpt2 and 3 → ChpArec phosphotransfer (red X) but continues to allow Hpt4–6 → ChpArec (green arrow) and ChpArec → Hpt2 and 3. The net result is dramatic increase in accumulation of phosphoryl groups on Hpt2 and 3.
