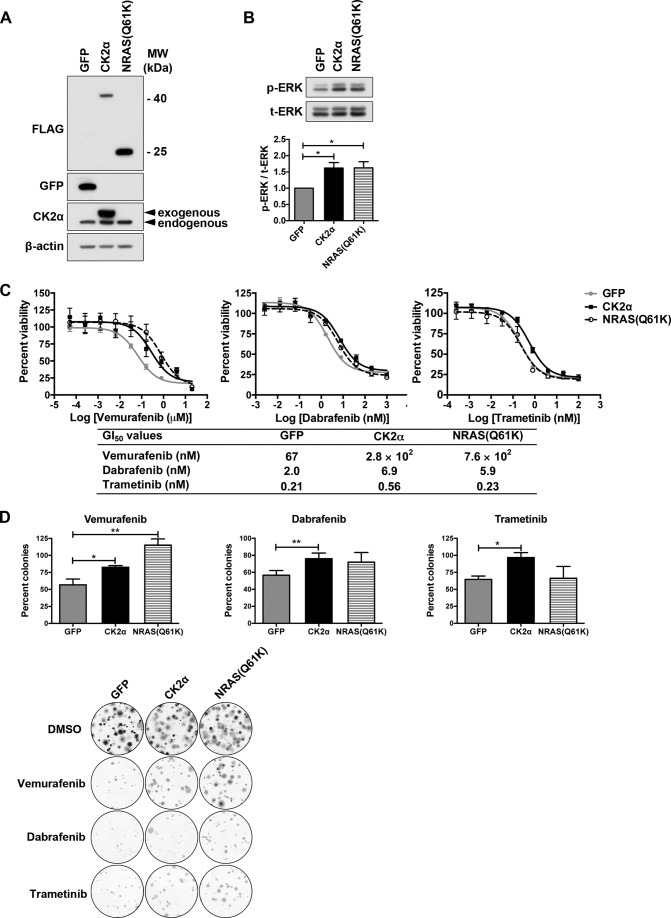
FIGURE 2.
Ectopic CK2α promotes resistance to inhibitors of BRAF and MEK. A, A375 cells were stably infected with lentiviral vectors to ectopically express GFP negative control or FLAG-tagged CK2α or NRAS(Q61K), and cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting using anti-FLAG, anti-GFP, and anti-CK2α antibodies. β-Actin served as a loading control. B, expression of CK2α or NRAS(Q61K) increases the basal level of ERK phosphorylation in A375 cells by 1.62-fold as determined by Western blotting using anti-phospho-ERK(Thr-202/Tyr-204) antibody and normalized to total ERK (t-ERK) (n = 5). C, CK2α increases GI50 for BRAFi vemurafenib, BRAFi dabrafenib, and MEKi trametinib. 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assays were performed after 72 h of treatment with nine different doses of inhibitors, and dose-response curves were generated by GraphPad Prism v5.0c. Results are presented as means ± S.E. (n = 6). A summary of all GI50 values is shown in the table below. D, CK2α enhances clonogenic survival of inhibitor-treated A375 cells. Cells as in the previous panels were grown for 2 weeks on plastic as single colonies in the presence of vemurafenib (1 μm), dabrafenib (100 nm), trametinib (1 nm), or DMSO vehicle control. Shown are the percentage of colonies formed in the presence of each inhibitor relative to the vehicle control. Results are presented as means ± S.E. **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05 (n = 3). Crystal violet-stained images of colonies are shown in the lower panel. Error bars represent S.E.