FIGURE 5.
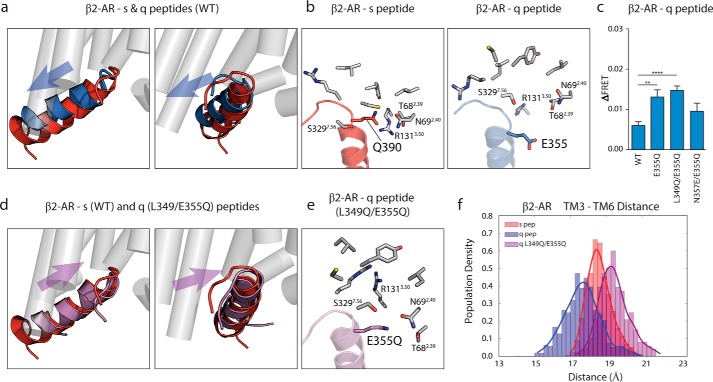
Glu-355 hot spot residue in q peptide shows steric clash in β2-AR interface, resolved by mutation to glutamine. a, overlain structures of s (red) and q (blue) peptides in β2-AR interface shows shallow rearranged orientation of q peptide compared with s peptide. b, intermolecular contacts (within 5 Å) made between Gln-390 of s peptide and β2-AR (left) are found outside of suitable binding (>6 Å) radius from Glu-355 in q peptide bound to β2-AR (right). c, ΔFRET assay with β2-AR testing E355Q q peptide mutant in context of single-point mutation, L349Q/E355Q double mutant, and E355Q/N357E double mutant compared with WT q peptide. d, double mutation of Glu-355 and Leu-349 in q peptide to glutamine rearranges mutant q peptide (purple) orientation to s peptide-like (red) orientation within β2-AR interface. e, several intermolecular contacts made between Gln-390 in s peptide and β2-AR are restored in the L349Q/E355Q q peptide interaction with β2-AR (highlighting E355Q residue). f, TM3 to TM6 distance measured in β2-AR bound to s, q, and q double mutant peptides. Results for ΔFRET are expressed as mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Asterisks represent significance of mutant peptides compared with WT peptide using Student unpaired t test. **, p ≤ 0.01; ****, p ≤ 0.0001.