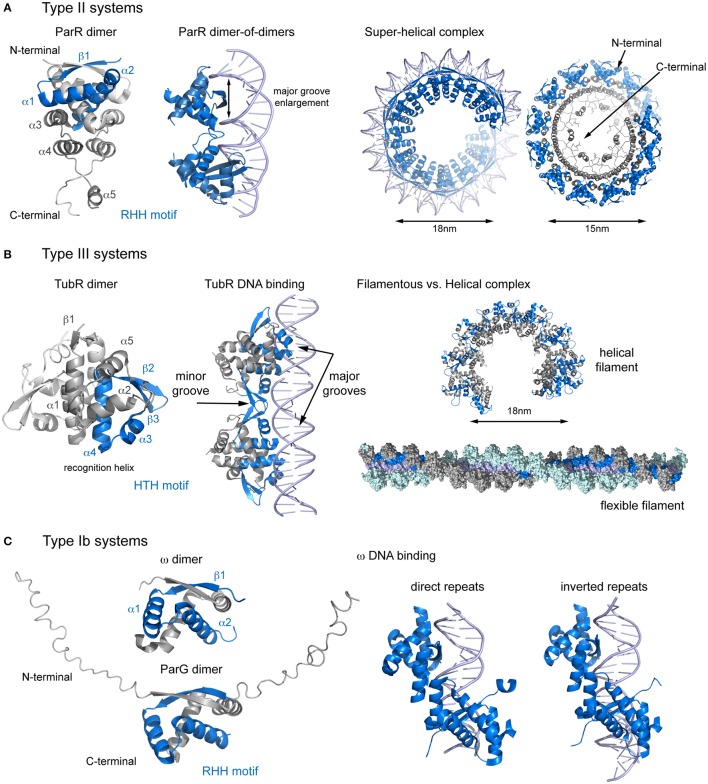
Figure 2.
Structural comparison of CBPs involved in segrosome assembly by wrapping. (A) Type II partition systems. Structure of ParR dimer (left), showing topology and the RHH motif; DNA changes upon ParR binding (middle), with enlargement of the DNA major groove; and formation of the the segrosome complex by DNA wrapping of the ParR super-helical oligomer (right), leaving the ParR C-terminal tail in the helix inside. (B) Type III partition systems. Structure of TubR dimer (left), showing topology and the HTH motif; the TubR-DNA binding mechanism (middle), in which the HTH makes contacts with the DNA major groove and the wing forms contacts with the minor groove; and putative filamentous vs. helical segrosome complexes (right), according to two crystal packing arrangements. (C) Type Ib partition systems. Structures of ParG and ω dimers (left), showing the RHH motif and the flexible N-terminal domain, and protein binding to direct and inverted repeats in equivalent ways (right).