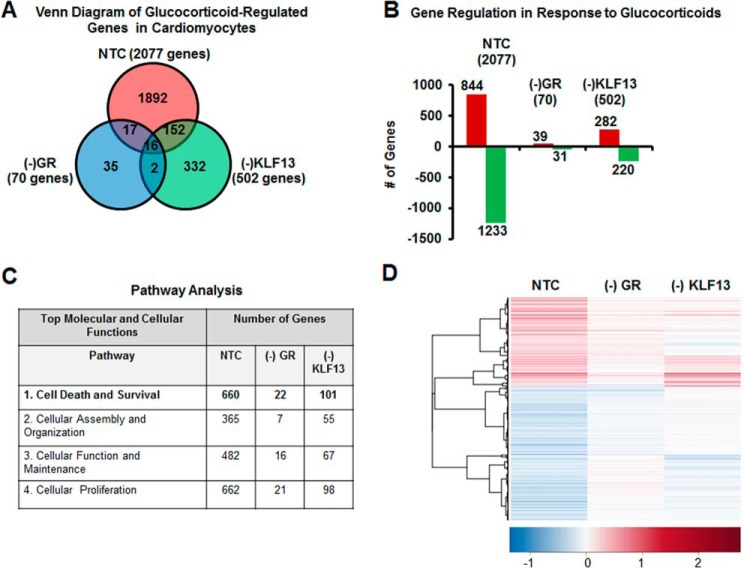
FIGURE 6.
KLF13 regulation by glucocorticoids is important to maintain cardiomyocytes global gene expression. HL-1 cells were transfected with non-target siRNA (NTC), GR siRNA ((−)GR), or KLF13 siRNA ((−)KLF13) and treated with vehicle-control (Veh) or 100 nm Dex. mRNA was isolated and analyzed using whole mouse genome 4 × 44 multiplex format oligo array (Agilent) for gene expression. A, the glucocorticoid-regulated genes within each group were sorted by a Venn diagram. B, the number of probes that were regulated by glucocorticoids is organized as either induced (red) or repressed (green) according to treatment group in NTC, (−)GR and (−)KLF13. C, results from microarray analysis of the glucocorticoid-regulated genes found in the three treatments were loaded into Ingenuity Pathway Analysis software. Glucocorticoid treatment significantly regulated an important number of genes associated to different cellular and molecular biological pathways. Silencing of GR and KLF13 by siRNA inhibited glucocorticoid regulation of the majority of these genes. Cell death and survival (bold letters) was ranked as the top 1 molecular and cellular function. D, glucocorticoid treatment regulated 660 genes associated to cell death and survival in NTC cells. Only 22 and 101 of these same genes were regulated in the absence of GR and KLF13, respectively. A heat map was generated with Heatplus software (BioConductor) to visualize the differences in the gene expression of cell death and survival genes between treatment groups.