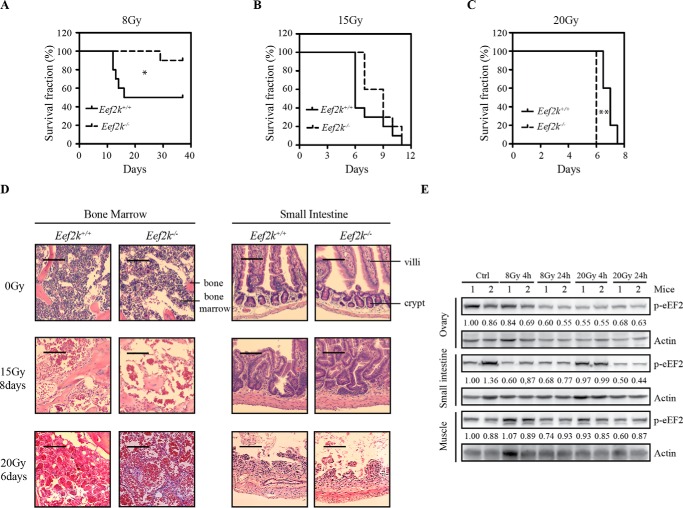
FIGURE 1.
Eef2k−/− mice displayed opposite sensitivities at low dose and high dose of ionizing radiation. A, Kaplan-Meier survival analyses of Eef2k+/+ and Eef2k−/− mice after 8-Gy total body γ-irradiation. Each group contained 10 mice. The p value was obtained by the log-rank test. B, Kaplan-Meier survival analyses of Eef2k+/+ and Eef2k−/− mice after 15-Gy total body γ-irradiation. Each group contained 10 mice. The p value was obtained by the log-rank test. C, Kaplan-Meier survival analyses of Eef2k+/+ and Eef2k−/− mice after 20-Gy total body γ-irradiation. Each group contained five mice. The p value was obtained by the log-rank test. D, H&E staining of autopsy samples from mouse bone marrow and small intestine tissues after mice succumbed to death after 0-, 15-, or 20-Gy total body γ-irradiation. Scale bars, 100 μm for 0-Gy tissue and 50 μm for other tissues. E, Western blotting analysis of p-eEF2 in ovary, small intestine, and muscle under normal conditions, after 8- and 20-Gy ionizing radiation. Actin was used as a loading control. Quantification was done by using Quantity One software. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.