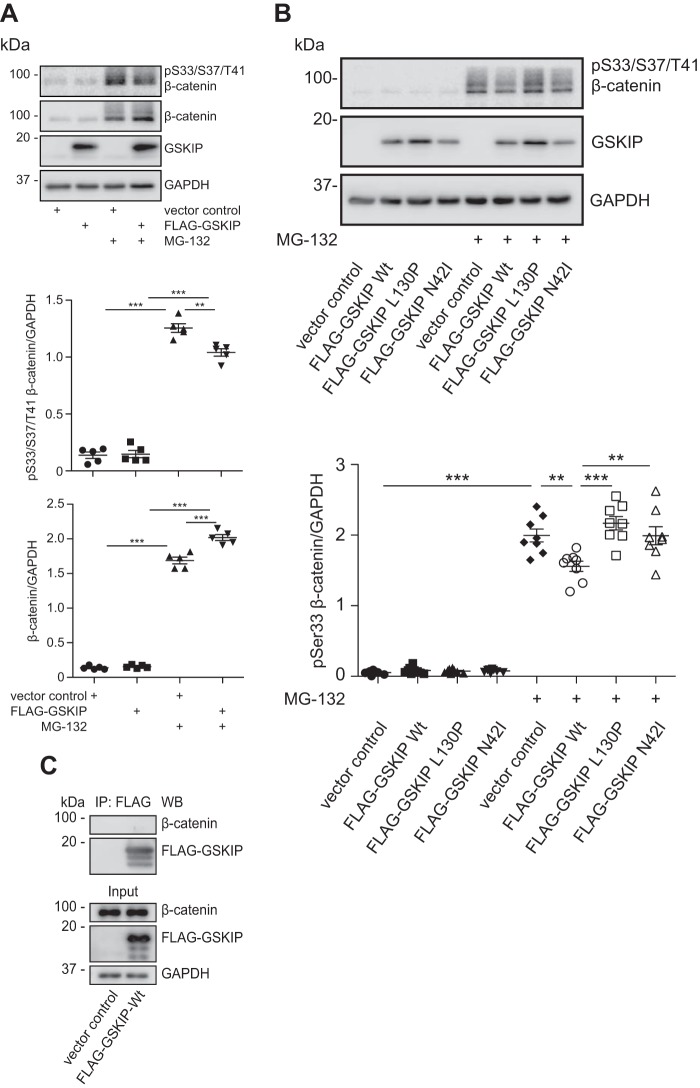
FIGURE 5.
Elevated levels of GSKIP enhance Wnt signaling through controlling the GSK3β-dependent phosphorylation of β-catenin at Ser-33/Ser-37/Thr-41. A, HEK293 cells expressing an empty vector control or wild type FLAG-GSKIP were left untreated or treated with the proteasome inhibitor, MG-132. Cytosolic fractions were purified, and the indicated proteins were detected by Western blotting. Semi-quantitative densitometric analyses of the signals depict the ratios of β-catenin to GAPDH and of (Ser(P)-33/Ser-37/Thr-41)-β-catenin to GAPDH; n = 5, mean ± S.E., ANOVA, **, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.001. pS33/S37/T41, Ser(P)-33/Ser-37/Thr-41. B, HEK293 cells expressing an empty vector control or the indicated FLAG-GSKIP variants were left untreated or treated with MG-132, and cytosolic fractions were purified and subjected to Western blotting. Semi-quantitative densitometric analysis of the signals is depicted as the ratio of (Ser(P)-33/Ser-37/Thr-41)-β-catenin to GAPDH; n = 8, mean ± S.E., ANOVA, **, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.001. C, GSKIP and β-catenin do not form a complex in cells. HEK293 cells expressing FLAG-GSKIP or an empty control vector were subjected to an immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG antibody. Precipitated FLAG-GSKIP and endogenous β-catenin were detected by Western blotting (WB).