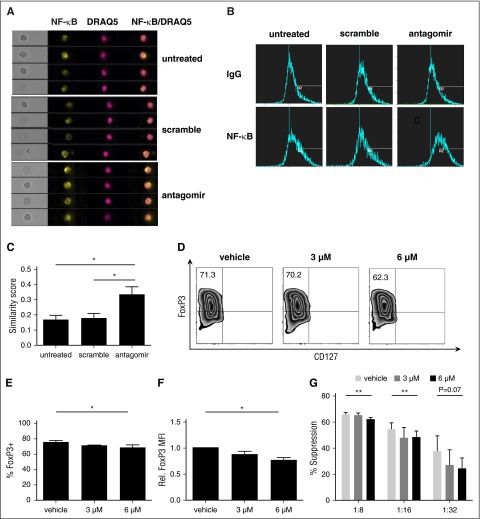
Figure 5.
NF-κB activation is essential for human tTreg development and translocating NF-κB to the nucleus after knockdown of miR-146b-5p (n = 3). Cells were left untreated or were incubated with scramble RNA or miR-146b antagomir. Following treatment, cells were stained for CD4, NF-κB, and DRAQ5 and NF-κB nuclear localization determined by imaging flow cytometry. (A) Representative Imagestream images of cultured tTregs showing bright-field images, as well as individual or overlaid images of NF-κB and DRAQ5. (B-C) Representative (B) or summary (C) of similarity score measured by IDEA software quantitating the degree of overlap between NF-κB and DRAQ5 staining. Higher similarity scores indicate increased nuclear localization. For panels D-G, naive peripheral blood tTregs were purified, expanded in vitro, and were treated with either DMSO only or PS1145. (D) Representative example of Foxp3 vs CD127 staining on tTreg (gated on CD4+ cells). (E) Summary of overall %Foxp3+CD127− cells, and (F) level of Foxp3 expression. (G) CFSE assay for suppressive function in tTregs from each group. Values indicate mean ± SEM of these experiments. *P < .05; **P < .01. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity.