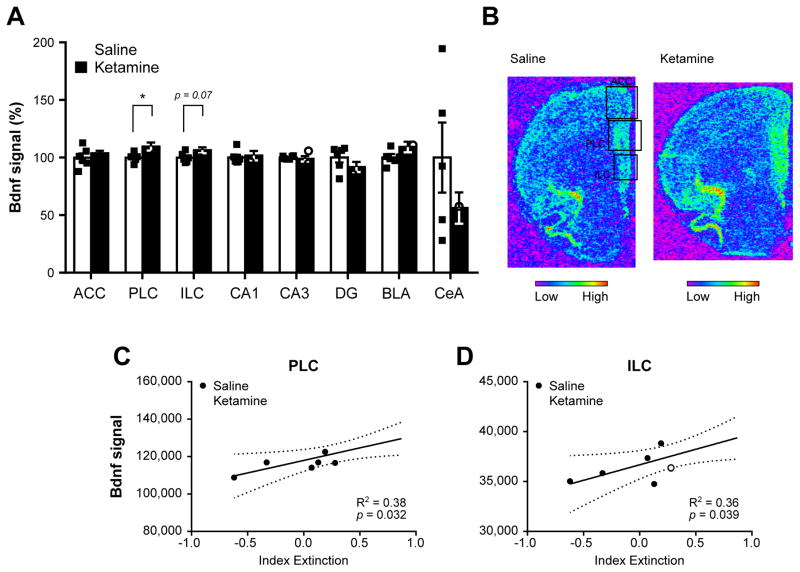
Figure 5.
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (Bdnf) expression profile in ketamine- and saline-treated animals following contextual fear memory reconsolidation test. The analysis of Bdnf mRNA levels by in situ hybridization in several subregions of the medial prefrontal cortex, hippocampus and amygdala (A) revealed an up-regulation of Bdnf in the prelimbic and infralimbic areas of the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). Representative pictures of Bdnf signal in saline-(top) and ketamine-treated (bottom) rats in the mPFC. Each square denotes the three mPFC areas quantified. Regression analyses between the extinction index depicted in Fig. 3C and Bdnf signal in the prelimbic (C) and infralimbic cortices (D) revealed a significant positive link between Bdnf signal in these areas and contextual fear memory extinction. In (A), each individual data point is depicted within column. *p < 0.05. ACC: anterior cingulate cortex, PLC: prelimbic cortex, ILC: infralimbic cortex, CA1: cornu ammonis 1, CA3: cornu ammonis 3, DG: dentate gyrus, BLA: basolateral amygdala, CeA: central amygdala. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.