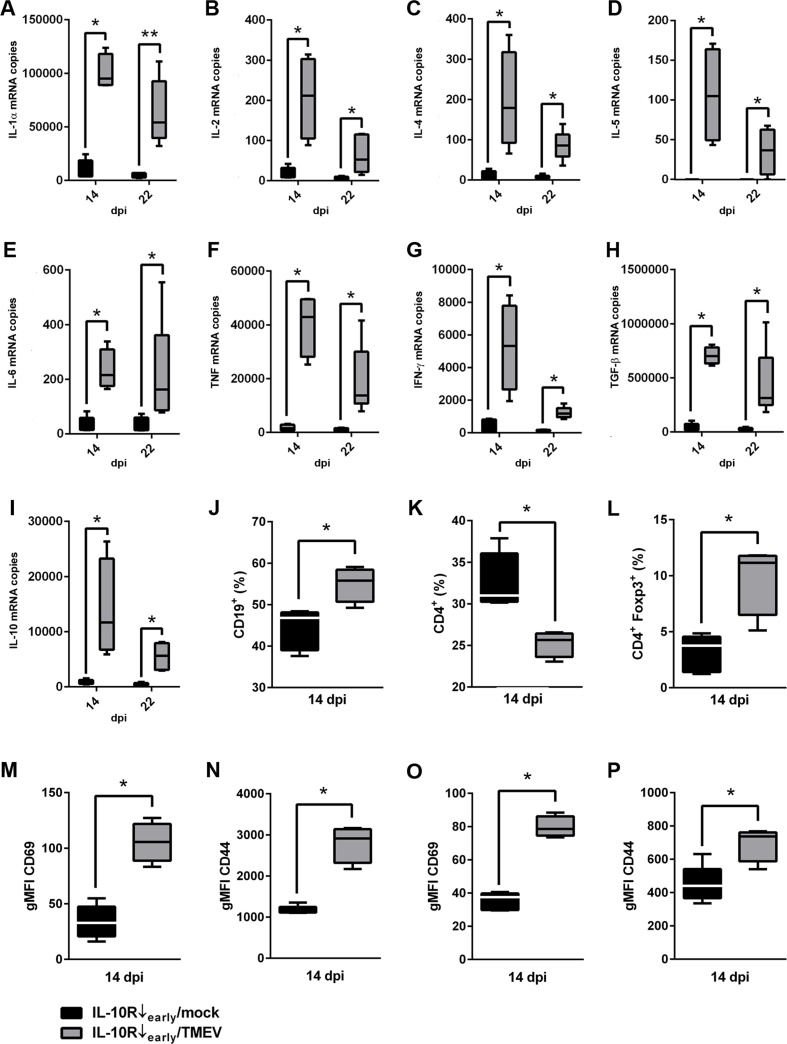
Fig 8. Effects of acute Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus (TMEV)-infection (experiment I) upon cytokine expression and phenotypical changes in spleens of interleukin-10 receptor (IL-10R) blocked SJL mice.
(A-I) Significantly elevated mRNA levels of IL-1α, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, TNF, IFN-γ, TGF-β and IL-10 in spleens of infected mice (group “IL-10R↓early/TMEV”) compared to non-infected animals following IL-10R antibody (Ab) treatment (group “IL10R↓early/mock”). (J) Flow cytometry revealed a relative increase of CD19+ B cells and a simultaneous decrease of CD4+ T cells (K) in the spleen of infected mice following IL-10R blockade at 14 dpi. (L) Additionally, the relative numbers of CD4+ Foxp3+ Treg in the spleen were increased following TMEV-infection and IL-10R blockade. Moreover, gMFI of CD69 (M) and CD44 (N) gated on CD4+ cells and gMFI of CD69 (O) and CD44 (P) gated on CD8+ cells were increased at 14 dpi in infected mice following IL-10R Ab treatment. For gating strategy see S1 Fig. IL-10R Ab treated animals without TMEV-infection (group “IL10R↓early/mock”). IL-10R Ab treated mice with additional TMEV-infection (group “IL-10R↓early/TMEV”). Box and whisker plots display median, minimum and maximum values as well as upper and lower quartiles, 5 animals used in both groups and at all investigated time points, Wilcoxon rank-sum tests, * = p < 0.05.