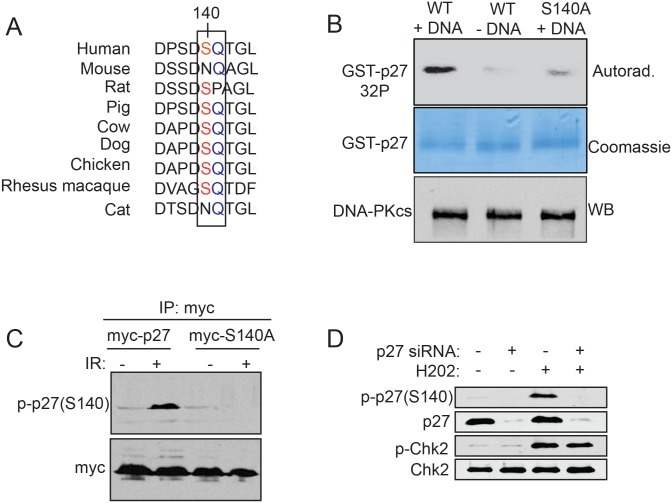
Fig 4. p27Kip1 is phosphorylated at Ser140 after induction of double-strand breaks.
(A) Sequence alignment of human p27Kip1 (residue 136 to 144) across 8 model organisms. The ATM/ATR/DNA-PK SQ phosphorylation consensus is boxed. (B) p27Kip1 in vitro phosphorylation assay. GST-p27WT or S140A was incubated with purified DNA-PK in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP. Calf thymus DNA was added to activate the kinase where indicated (+DNA). A portion of the reaction was separated on SDS-PAGE and analyzed by autoradiography and another portion was separated on SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting with a DNA-PK antibody. (C) Specificity assessment of the p-p27(S140) antibody. MCF7 cells were transfected with either, empty vector (myc), myc-p27 or myc-p27S140A expressing constructs and subjected to 0 (-) or 6 Gy (+) of IR. 1 hour post IR, ectopically expressed p27Kip1 was immunoprecipitated with an anti-myc antibody and phosphorylation of p27Kip1 at S140 was assessed by Western blotting using a p27 S140 phospho-specific antibody (p-p27(S140)) as indicated on the left of the panel. (D) MCF7 cells were transfected with non-targeting control (-) or p27 siRNAs (+) for 72h before treatment with H2O2 (0.2 mM) for 1h to induce DNA double-strand breaks. Cells were processed for Western blotting analysis with specific antibodies as indicated on the left of each panel. All the panels from this figure are representative of 3 independent experiments.