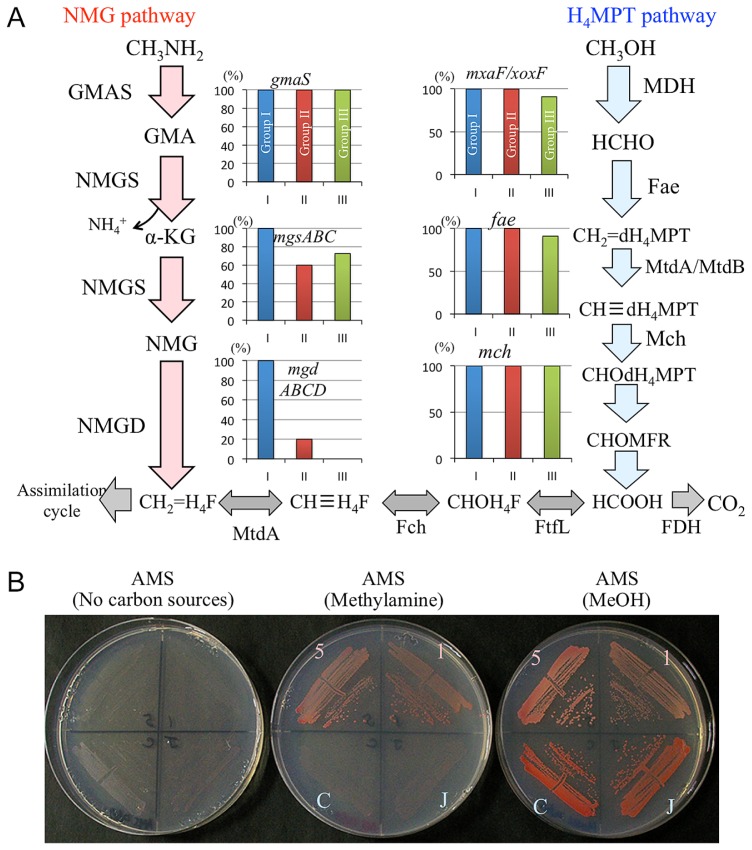
Fig. 4.
Distribution of genes involved in methylamine and methanol metabolism among Methylobacterium species and the ability of Methylobacterium strains to use methylamine and methanol as sole carbon sources. (A) Percentage of strains in each group that have genes responsible for each step; pathway maps are shown next to the graphs. Abbreviations for enzymes: Fae, formaldehyde-activating enzyme; Fch, methenyl-H4F cyclohydrolase; FDH, formate dehydrogenase; Fhc, formyltransferase/hydrolase complex; FtfL, formate-tetrahydrofolate ligase; Mch, methenyl-dH4MPT cyclohydrolase; MDH, methanol dehydrogenase; MtdA and MtdB, methylene-tetrahydromethanopterin dehydrogenase. Abbreviations for compounds: CH2=dH4MPT, methylene-dH4MPT; CH≡dH4MPT, methenyl-dephospho H4MPT; CHOdH4MPT, formyl dH4MPT; MFR, methanofuran; CHOMFR, formyl-MFR; H4F, tetrahydrofolate; CHOH4F, formyl-H4F; CH≡H4F, methenyl H4F; dH4MPT, dephosphotetrahydromethanopterin; GMA, γ-glutamylmethylamide; NMG, N-methylglutamate; α-KG, α-ketoglutarate. (B) Growth test without a carbon source or with methylamine or methanol as the sole carbon source for 7 d. 5, Methylobacterium sp. AMS5 (Group I); 1, M. extorquens AM1 (Group I); C, M. oryzae CBMB20 (Group III); J, M. radiotolerans JCM2831 (Group III).