Fig. 1. The KCNE3 protein and its function.
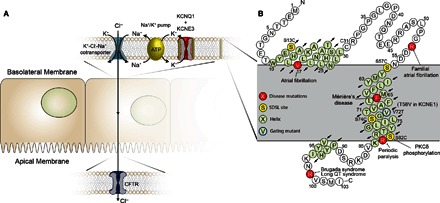
(A) Role of the KCNQ1-KCNE3 channel complex in chloride ion secretion. KCNE3 modulates the voltage-gated potassium channel KCNQ1, removing voltage-dependent gating, leading to a constitutively open leak channel. The KCNQ1-KCNE3 complex is expressed in basolateral epithelial membranes, where it plays a role in K+ recycling necessary for Cl− secretion across the apical membrane. Disruptions in transepithelial Cl− transport are involved in human pathologies, such as CF and cholera. (B) Sequence and membrane topology of KCNE3. The α-helical regions determined by NMR are highlighted in light green. Sites of disease-linked mutations are highlighted in red, whereas yellow sites were mutated to cysteine and spin-labeled to enable PRE NMR distance measurements. SDSL, site-directed spin labeling; PKCδ, protein kinase Cδ.
