Fig. 6. Pairwise replacement of sites 240 + 244 or 241 + 244 in the S4 domain of KCNQ1 with the corresponding residues of KCNQ4 causes KCNQ1 to be inhibited by KCNE3.
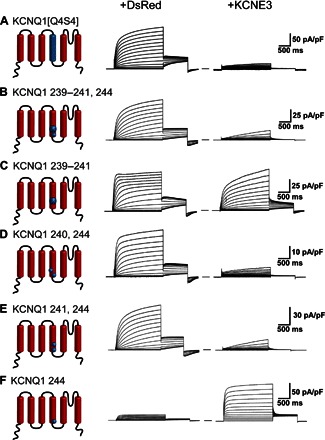
Average whole-cell currents recorded from cells transiently expressing KCNQ1 mutants or KCNQ4 chimeras, both alone (+DsRed) and with KCNE3: (A) KCNQ1 with the S4 domain of KCNQ4 (KCNQ1[Q4S4]); (B) Leu239Val,His240Arg,Val241Met,Gln244Arg KCNQ1; (C) Leu239Val,His240Arg,Val241Met KCNQ1; (D) His240Arg,Gln244Arg KCNQ1; (E) Val241Met,Gln244Arg KCNQ1; and (F) Gln244Arg KCNQ1. We note that the His240Arg, Gln244Arg KCNQ1, and Gln244Arg KCNQ1 mutants have been previously examined (36), with somewhat different results being obtained. However, our studies were conducted using CHO cells, which are bereft of endogenous expression of KCNE subunits, whereas the previous studies were conducted using KCNQ1 expressed in oocytes, in which the expression of either endogenous KCNE subunits or endogenous K+ channels can confound studies of potassium channels (75–77).
