Abstract
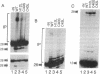
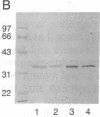
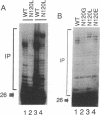
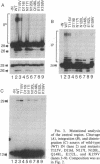
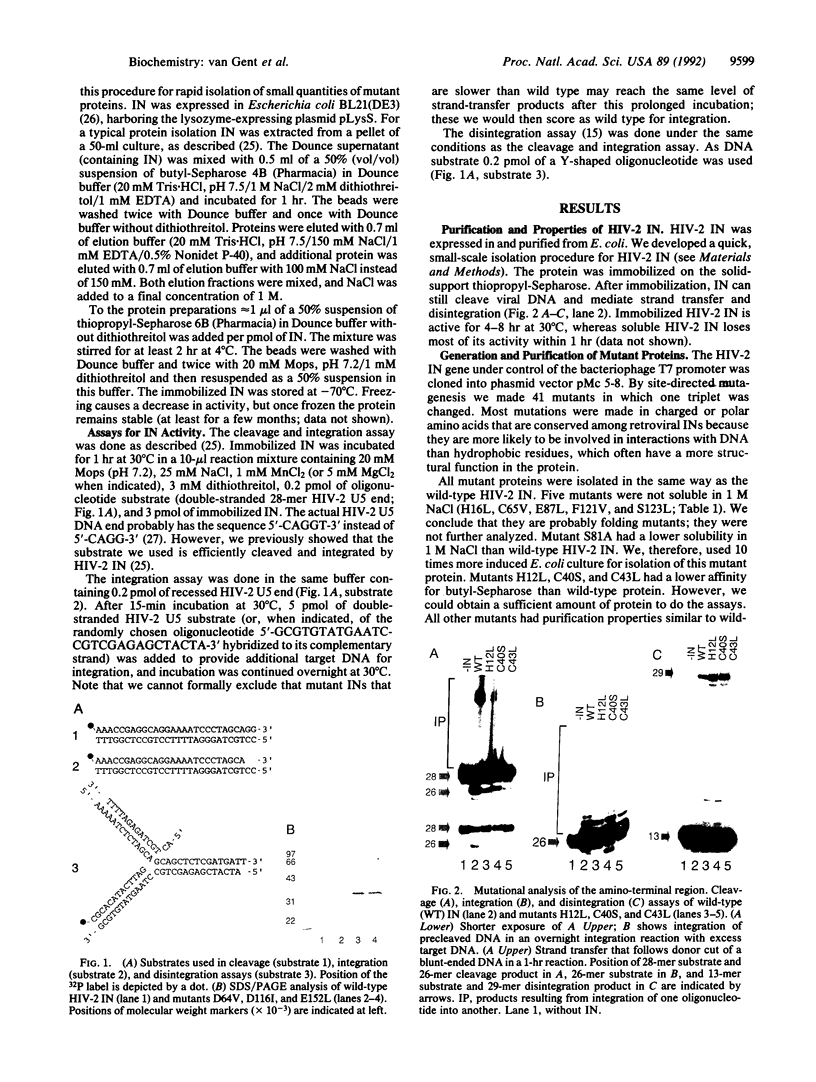
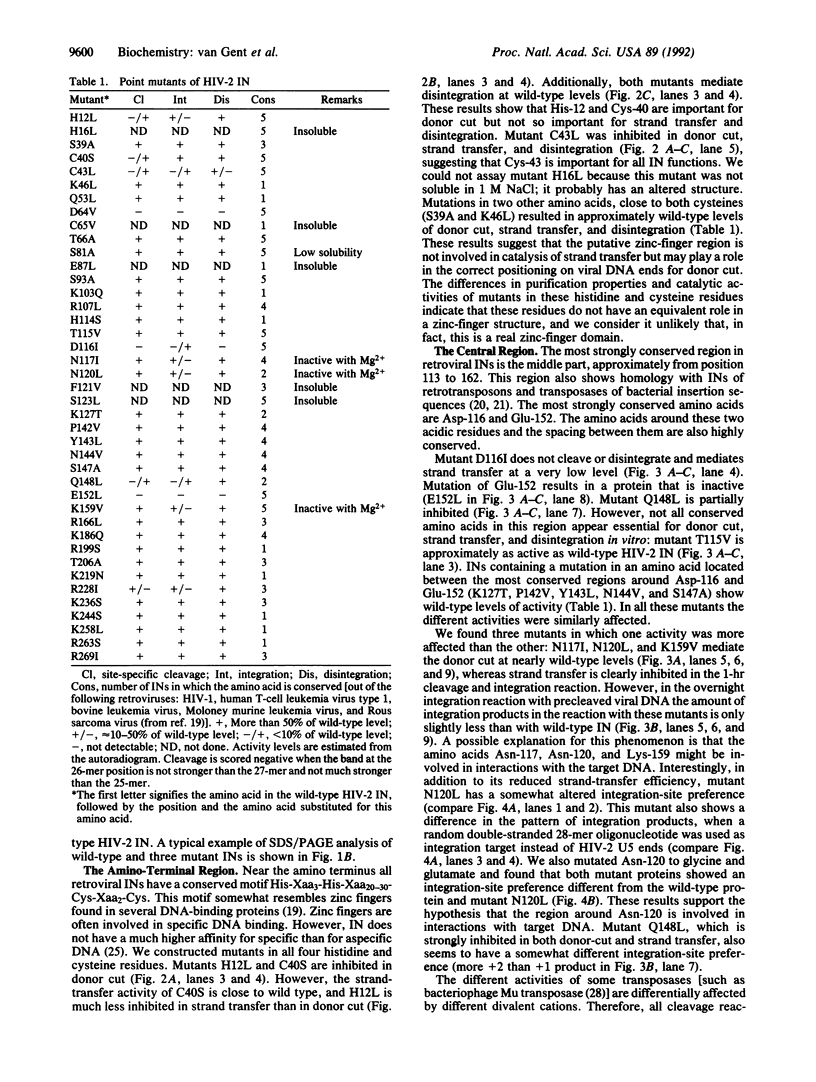
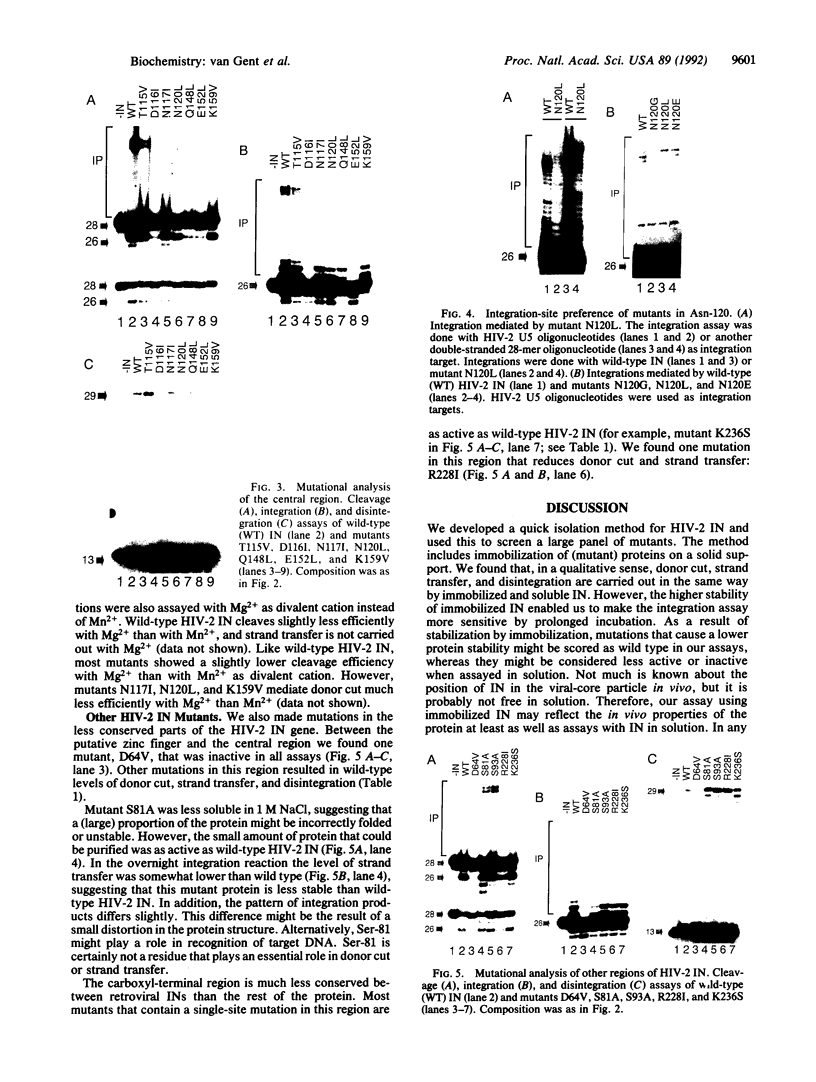
Purified integrase protein (IN) can nick linear viral DNA at a specific site near the ends and integrate nicked viral DNA into target DNA. We have made a series of 43 site-directed point mutants of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 IN and assayed purified mutant proteins for the following activities: site-specific cleavage of viral DNA (donor cut), integration (strand transfer), and disintegration. In general, the different activities were similarly affected by the mutations. We found three mutations that (almost) totally abolished IN function: Asp-64-->Val, Asp-116-->Ile, and Glu-152-->Leu, whereas 25 mutations did not affect IN function. A few mutations affected the different activities differentially. Near the amino terminus a zinc finger-like sequence motif His-Xaa3-His-Xaa20-30-Cys-Xaa2-Cys is present in all retroviral IN proteins. Two mutations in this region (His-12-->Leu and Cys-40-->Ser) strongly inhibited donor cut but had less effect on strand transfer. The central region of IN is most highly conserved between retroviral INs. Three mutants in this region (Asn-117-->Ile, Asn-120-->Leu, and Lys-159-->Val) were inhibited in strand transfer but were inhibited less strongly in donor cut. Mutation of Asn-120 (to glycine, leucine, or glutamate) resulted in changes in integration-site preference, suggesting that Asn-120 is involved in interactions with target DNA. We did not find a mutant in which one activity was lost and the others were unaffected, supporting the notion that IN has only one active site for the catalysis of donor cut and strand transfer.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker T. A., Mizuuchi M., Mizuuchi K. MuB protein allosterically activates strand transfer by the transposase of phage Mu. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1003–1013. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90552-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Correct integration of retroviral DNA in vitro. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Retroviral integration: structure of the initial covalent product and its precursor, and a role for the viral IN protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2525–2529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Craigie R. Activities of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) integration protein in vitro: specific cleavage and integration of HIV DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1339–1343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow S. A., Vincent K. A., Ellison V., Brown P. O. Reversal of integration and DNA splicing mediated by integrase of human immunodeficiency virus. Science. 1992 Feb 7;255(5045):723–726. doi: 10.1126/science.1738845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Fujiwara T., Bushman F. The IN protein of Moloney murine leukemia virus processes the viral DNA ends and accomplishes their integration in vitro. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):829–837. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90126-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drelich M., Wilhelm R., Mous J. Identification of amino acid residues critical for endonuclease and integration activities of HIV-1 IN protein in vitro. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90499-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman A., Mizuuchi K., Craigie R. HIV-1 DNA integration: mechanism of viral DNA cleavage and DNA strand transfer. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1211–1221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90297-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayet O., Ramond P., Polard P., Prère M. F., Chandler M. Functional similarities between retroviruses and the IS3 family of bacterial insertion sequences? Mol Microbiol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1771–1777. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00555.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Mizuuchi K. Retroviral DNA integration: structure of an integration intermediate. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. S., McClure M. A., Feng D. F., Gray J., Doolittle R. F. Computer analysis of retroviral pol genes: assignment of enzymatic functions to specific sequences and homologies with nonviral enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7648–7652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. A., Mack J. P., Merkel G., Kulkosky J., Ge Z., Leis J., Skalka A. M. Requirement for a conserved serine in both processing and joining activities of retroviral integrase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6741–6745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. A., Merkel G., Kulkosky J., Leis J., Skalka A. M. The avian retroviral IN protein is both necessary and sufficient for integrative recombination in vitro. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90290-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman M., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M., Leis J. The avian retroviral integration protein cleaves the terminal sequences of linear viral DNA at the in vivo sites of integration. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5319–5327. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5319-5327.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan E., Mack J. P., Katz R. A., Kulkosky J., Skalka A. M. Retroviral integrase domains: DNA binding and the recognition of LTR sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):851–860. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFemina R. L., Callahan P. L., Cordingley M. G. Substrate specificity of recombinant human immunodeficiency virus integrase protein. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5624–5630. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5624-5630.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt A. D., Rose R. B., Varmus H. E. Both substrate and target oligonucleotide sequences affect in vitro integration mediated by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase protein produced in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2359–2368. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2359-2368.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. J., Schwartzberg P. L., Goff S. P. Structure of the termini of DNA intermediates in the integration of retroviral DNA: dependence on IN function and terminal DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzberg P., Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Construction and analysis of deletion mutations in the pol gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus: a new viral function required for productive infection. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1043–1052. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90439-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Fyfe J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus integration protein expressed in Escherichia coli possesses selective DNA cleaving activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5119–5123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanssens P., Opsomer C., McKeown Y. M., Kramer W., Zabeau M., Fritz H. J. Efficient oligonucleotide-directed construction of mutations in expression vectors by the gapped duplex DNA method using alternating selectable markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4441–4454. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., Yeheskiely E., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Plasterk R. H. Site-specific hydrolysis and alcoholysis of human immunodeficiency virus DNA termini mediated by the viral integrase protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6691–6698. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., van Gent D. C., Elgersma Y., Plasterk R. H. Human immunodeficiency virus integrase protein requires a subterminal position of its viral DNA recognition sequence for efficient cleavage. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4636–4644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4636-4644.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vora A. C., Fitzgerald M. L., Grandgenett D. P. Removal of 3'-OH-terminal nucleotides from blunt-ended long terminal repeat termini by the avian retrovirus integration protein. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5656–5659. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5656-5659.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitcomb J. M., Hughes S. H. The sequence of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 circle junction suggests that integration protein cleaves the ends of linear DNA asymmetrically. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3906–3910. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3906-3910.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberger C., Vershon A. K., Liu B., Johnson A. D., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of a MAT alpha 2 homeodomain-operator complex suggests a general model for homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90526-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gent D. C., Elgersma Y., Bolk M. W., Vink C., Plasterk R. H. DNA binding properties of the integrase proteins of human immunodeficiency viruses types 1 and 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3821–3827. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]