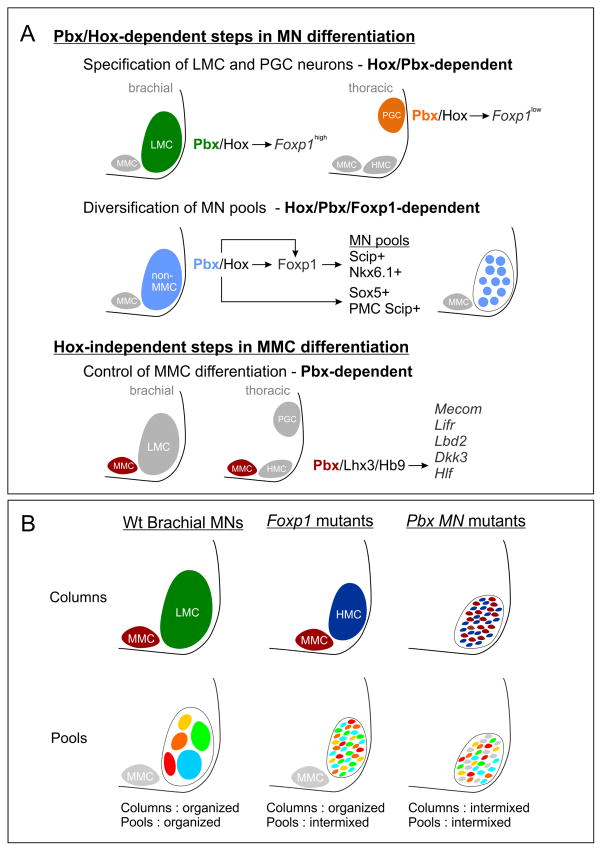
Figure 8. Pbx Genes Function in Parallel MN Differentiation Pathways.
(A) Pbx genes are essential for Hox-dependent and -independent steps in MN differentiation. Pbx genes are required for two critical Hox-dependent steps: the specification of LMC and PGC columnar subtypes, and the diversification of LMC motor pools. Pbx genes are also necessary for the maturation of MMC neurons and govern expression of a subset of MMC-restricted genes, including Mecom. (B) Summary of defects in MN organization in Foxp1 and Pbx mutants at brachial levels. MN organization in wildtype (Wt) mice at brachial levels is shown. In Foxp1 mutants LMC neurons revert to an HMC-like identity but are clustered and segregated from MMC neurons. However, the position of MN pools projecting to individual muscles is disordered. In Pbx mutants the remaining HMC and MMC neurons are intermixed, leading to severe defects in MN clustering.