Figure 4.
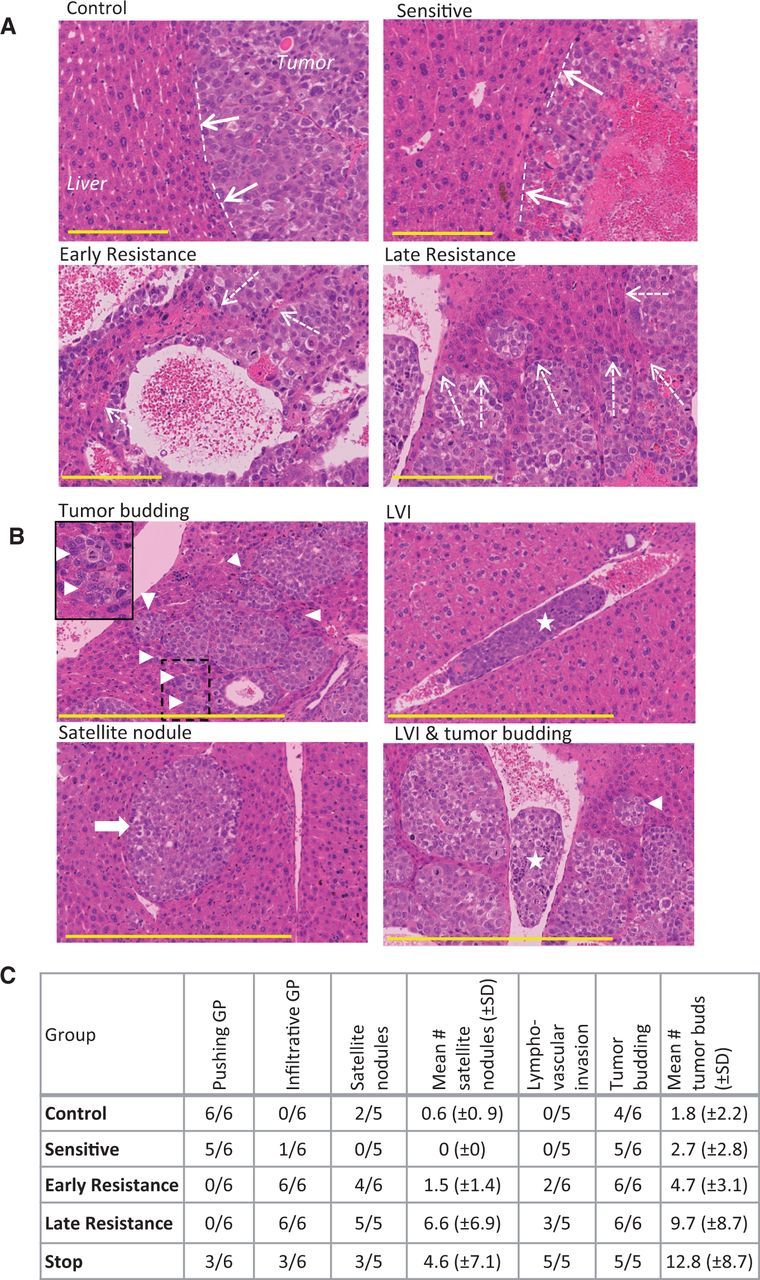
Histopathological signs of invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) xenografts. A) Tumor growth patterns were predominantly pushing in control and sensitive tumors (dashed lines and solid arrows) and were mostly infiltrative growth (resistance phases), leading to tumor incorporation of liver parenchyma (dashed arrows). Tumors were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. B) Tumor budding (triangle; box demonstrates magnified area), lymphovascular invasion (LVI; star), and satellite nodules (arrow), additional signs of tumor aggressiveness, were common in resistant tumors. C) The prevalence of some of the invasive tumor features tended to increase from control and sensitive to resistant tumors, with a mixed phenotype in stop group tumors. (n = 6 per group). Scale bar = 200 µm. GP = growth pattern.
